Antibody response after one and two jabs of the BNT162b2 vaccine in nursing home residents: The CONsort-19 study
- PMID: 34286856
- PMCID: PMC8441741
- DOI: 10.1111/all.15007
Antibody response after one and two jabs of the BNT162b2 vaccine in nursing home residents: The CONsort-19 study
Abstract
Background: The humoral immune response following COVID-19 vaccination in nursing home residents is poorly known. A longitudinal study compared levels of IgG antibodies against the spike protein (S-RBD IgG) (S-RDB protein IgG) after one and two BNT162b2/Pfizer jabs in residents with and without prior COVID-19.
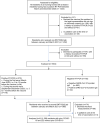
Methods: In 22 French nursing homes, COVID-19 was diagnosed with real-time reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) for SARS-CoV-2. Blood S-RDB-protein IgG and nucleocapsid (N) IgG protein (N-protein IgG) were measured 21-24 days after the first jab (1,004 residents) and 6 weeks after the second (820 residents).
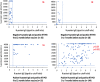
Results: In 735 residents without prior COVID-19, 41.7% remained seronegative for S-RDB-protein IgG after the first jab vs. 2.1% of the 270 RT-PCR-positive residents (p < 0.001). After the second jab, 3% of the 586 residents without prior COVID-19 remained seronegative. However, 26.5% had low S-RDB-protein IgG levels (50-1050 UA/ml) vs. 6.4% of the 222 residents with prior COVID-19. Residents with an older infection (first wave), or with N-protein IgG at the time of vaccination, had the highest S-RDB-protein IgG levels. Residents with a prior COVID-19 infection had higher S-RDB-protein IgG levels after one jab than those without after two jabs.
Interpretation: A single vaccine jab is sufficient to reach a high humoral immune response in residents with prior COVID-19. Most residents without prior COVID-19 are seropositive for S-RDB-protein IgG after the second jab, but around 30% have low levels. Whether residents with no or low post-vaccine S-RDB protein IgG are at higher risk of symptomatic COVID-19 requires further analysis.
Keywords: BNT162b2/Pfizer vaccine; COVID-19; antibodies against SARS-CoV-2; nursing home; rRT-PCR.
© 2021 European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest/competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
T-Cell Mediated Response after Primary and Booster SARS-CoV-2 Messenger RNA Vaccination in Nursing Home Residents.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2023 Feb;24(2):140-147.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2022.11.024. Epub 2022 Dec 7. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2023. PMID: 36587928 Free PMC article.
-
Strong Decay of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antibodies after 2 BNT162b2 Vaccine Doses and High Antibody Response to a Third Dose in Nursing Home Residents.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2022 May;23(5):750-753. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2022.02.006. Epub 2022 Feb 23. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2022. PMID: 35311651 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor binding domain-IgG levels correlate with protection in residents facing SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 outbreaks.Allergy. 2022 Jun;77(6):1885-1894. doi: 10.1111/all.15142. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Allergy. 2022. PMID: 34652831 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody response after first and second BNT162b2 vaccination to predict the need for subsequent injections in nursing home residents.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 12;12(1):13749. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18041-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35962053 Free PMC article.
-
Pronounced antibody elevation after SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 mRNA booster vaccination in nursing home residents.Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2022 Nov;16(6):1066-1071. doi: 10.1111/irv.13030. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35962568 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Humoral and Cellular Responses to COVID-19 Vaccination Indicate the Need for Post-Vaccination Testing in Frail Population.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Feb 8;10(2):260. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10020260. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214717 Free PMC article.
-
T-Cell Mediated Response after Primary and Booster SARS-CoV-2 Messenger RNA Vaccination in Nursing Home Residents.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2023 Feb;24(2):140-147.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2022.11.024. Epub 2022 Dec 7. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2023. PMID: 36587928 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 in French nursing homes during the second pandemic wave: a mixed-methods cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2022 Sep 20;12(9):e060276. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-060276. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36127110 Free PMC article.
-
Serological Responses up to 9 Months following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination in Residents and Health-Care Workers of Long-Term Care Facilities: A Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study in Northern Italy.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Dec 19;10(12):2183. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10122183. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36560593 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 mRNA Based Vaccine Immune-Response Assessment in Nursing Home Residents for Public Health Decision.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Dec 2;9(12):1429. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9121429. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34960173 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

