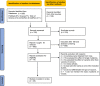
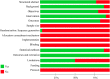
Potency of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 vaccine-induced neutralizing antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome-CoV-2 variants of concern: A systematic review of in vitro studies
- PMID: 34286893
- PMCID: PMC8420542
- DOI: 10.1002/rmv.2277
Potency of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 vaccine-induced neutralizing antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome-CoV-2 variants of concern: A systematic review of in vitro studies
Abstract
BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 are two types of mRNA-based vaccine platforms that have received emergency use authorization. The emergence of novel severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV-2) variants has raised concerns of reduced sensitivity to neutralization by their elicited antibodies. We aimed to systematically review the most recent in vitro studies evaluating the effectiveness of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 induced neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. We searched PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science in addition to bioRxiv and medRxiv with terms including 'SARS-CoV-2', 'BNT162b2', 'mRNA-1273', and 'neutralizing antibody' up to June 29, 2021. A modified version of the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) checklist was used for assessing included study quality. A total 36 in vitro studies meeting the eligibility criteria were included in this systematic review. B.1.1.7 (Alpha), B.1.351 (Beta), P.1 (Gamma), and B.1.617.2 (Delta) are four SARS-CoV-2 variants that have recently been identified as variants of concern. Included studies implemented different methods regarding pseudovirus or live virus neutralization assays for measuring neutralization titres against utilized viruses. After two dose vaccination by BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273, the B.1.351 variant had the least sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies, while B.1.1.7 variant had the most sensitivity; that is, it was better neutralized relative to the comparator strain. P.1 and B.1.617.2 variants had an intermediate level of impaired naturalization activity of antibodies elicited by prior vaccination. Our review suggests that immune sera derived from vaccinated individuals might show reduced protection of individuals immunized with mRNA vaccines against more recent SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern.
Keywords: BNT162b2; SARS-CoV-2; mRNA-1273; neutralizing antibody; variants of concern.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID‐19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/
-
- EUA AT, Agnihothram S. Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for an unapproved product review memorandum identifying information.
-
- WHO lists Moderna vaccine for emergency use. https://www.who.int/news/item/30‐04‐2021‐who‐lists‐moderna‐vaccine‐for‐e...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous