Costs and Outcomes of Integrated Human African Trypanosomiasis Surveillance System Using Rapid Diagnostic Tests, Democratic Republic of the Congo
- PMID: 34287133
- PMCID: PMC8314840
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2708.202399
Costs and Outcomes of Integrated Human African Trypanosomiasis Surveillance System Using Rapid Diagnostic Tests, Democratic Republic of the Congo
Abstract
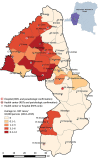
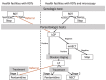
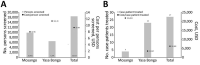
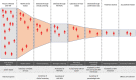
We integrated sleeping sickness case detection into the primary healthcare system in 2 health districts in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. We replaced a less field-friendly serologic test with a rapid diagnostic test, which was followed up by human African trypanosomiasis microscopic testing, and used a mixed costing methodology to estimate costs from a healthcare provider perspective. We screened a total of 18,225 persons and identified 27 new cases. Average financial cost (i.e., actual expenditures) was US $6.70/person screened and $4,464/case diagnosed and treated. Average economic cost (i.e., value of resources foregone that could have been used for other purposes) was $9.40/person screened and $6,138/case diagnosed and treated. Our study shows that integrating sleeping sickness surveillance into the primary healthcare system is feasible and highlights challenges in completing the diagnostic referral process and developing a context-adapted diagnostic algorithm for the large-scale implementation of this strategy in a sustainable and low-cost manner.
Keywords: Democratic Republic of the Congo; costs; diagnosis; human African trypanosomiasis; integration; parasites; primary health services; sleeping sickness; surveillance.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Factsheets: Trypanosomiasis, human African (sleeping sickness) [cited 2019 Apr 11]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/trypanosomiasis-human-a...
-
- Programme National de Lutte contre la Trypanosomiase Humaine Africaine en République Démocratique Du Congo. Database HAT cases: 2013–2017. Kinshasa (Democratic Republic of the Congo): The Programme; 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

