Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Mild COVID-19: Case Series and Analysis of the Literature
- PMID: 34287226
- PMCID: PMC8293051
- DOI: 10.3390/audiolres11030029
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Mild COVID-19: Case Series and Analysis of the Literature
Abstract
Background: There is growing evidence of otoneurological involvement of SARS-CoV-2, such as tinnitus and balance disorders and smell and taste disorders, but HL in COVID-19 patients has still been marginally studied. Investigating the role of SARS-CoV-2 as an aetiological factor of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SSNHL) may offer the opportunity to address treatment strategies to maximize clinical recovery and avoid side effects.
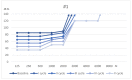
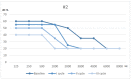
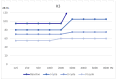
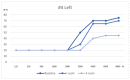
Methods and results: For this purpose, we will present case studies of five patients who experienced SSNHL during COVID-19. Patients were selected from COVID-19 positive adult subjects with mild clinical presentation, admitted to the outpatient Ear Nose and Throat Department of Cardarelli Hospital due to the onset of SSNHL during the infection. All underwent a complete audio-vestibular investigation before and after SSNHL treatment protocol. Each patient is described with a detailed analysis.
Conclusions: SSNHL could be an occasional symptom of COVID-19, even in mild manifestations of the disease. Our experience leads us to underline the value of promptly recognizing and addressing this and other uncommon symptoms, giving patients the opportunity to receive early treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; SSNHL; coronavirus; hearing loss; sudden sensorineural hearing loss; tinnitus; treatment; vertigo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Could sudden sensorineural hearing loss be the sole manifestation of COVID-19? An investigation into SARS-COV-2 in the etiology of sudden sensorineural hearing loss.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Aug;97:208-211. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.023. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32535294 Free PMC article.
-
No COVID-19 in Patients With Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SSNHL).Otol Neurotol. 2022 Feb 1;43(2):170-173. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000003438. Otol Neurotol. 2022. PMID: 34889826
-
COVID-19 and Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review.Front Neurol. 2022 Apr 28;13:883749. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.883749. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35572936 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Associated With COVID-19 Infection.Cureus. 2021 Nov 19;13(11):e19757. doi: 10.7759/cureus.19757. eCollection 2021 Nov. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34938632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19-related sudden sensorineural hearing loss.Qatar Med J. 2021 Oct 25;2021(3):58. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2021.58. eCollection 2021. Qatar Med J. 2021. PMID: 34745911 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A review on the impacts of COVID-19 on the auditory system: Implications for public health promotion research.Health Promot Perspect. 2023 Dec 16;13(4):280-289. doi: 10.34172/hpp.2023.33. eCollection 2023. Health Promot Perspect. 2023. PMID: 38235010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of Ginkgo biloba extract as an adjuvant in the treatment of Chinese patients with sudden hearing loss: a meta-analysis.Pharm Biol. 2023 Dec;61(1):610-620. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2023.2190782. Pharm Biol. 2023. PMID: 36999358 Free PMC article.
-
Cochleovestibular findings linked to COVID-19: A scoping review for clinical care planning in South Africa.S Afr J Commun Disord. 2022 Aug 12;69(2):e1-e12. doi: 10.4102/sajcd.v69i2.899. S Afr J Commun Disord. 2022. PMID: 36073075 Free PMC article.
-
Vestibular Cochlear Manifestations in COVID-19 Cases.Front Neurol. 2022 Mar 18;13:850337. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.850337. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35370886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Dec 12;12(12):3139. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12123139. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553146 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

