Age-Dependent Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 and P.1 Variant by Vaccine Immune Serum Samples
- PMID: 34287620
- PMCID: PMC8295896
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2021.11656
Age-Dependent Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 and P.1 Variant by Vaccine Immune Serum Samples
Abstract
This study examines the relationship between age and neutralizing antibody titers against the SARS-CoV-2 USA-WA1/2020 strain and the P.1 variant after 2 doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
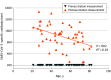
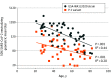
References
-
- Haas EJ, Angulo FJ, McLaughlin JM, et al. . Impact and effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 cases, hospitalisations, and deaths following a nationwide vaccination campaign in Israel: an observational study using national surveillance data. Lancet. 2021;397(10287):1819-1829. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00947-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

