Paraneoplastic myelitis associated with durvalumab treatment for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 34287773
- PMCID: PMC8763935
- DOI: 10.1007/s10637-021-01154-x
Paraneoplastic myelitis associated with durvalumab treatment for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer
Abstract
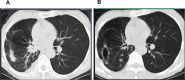
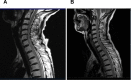
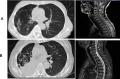
Paraneoplastic neurologic syndromes(PNSs) caused by immune checkpoint inhibitors(ICIs) is rare and requires clinicians to differentiate between disease progression and immune-related adverse effects(irAEs). We hereby report the case of immune-related myelitis accompanied by positive paraneoplastic autoantibodies following durvalumab treatment for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). A 70-year-old Chinese woman with ES-SCLC was administered durvalumab with etoposid-platinum(EP) as first-line treatment. Four cycles after treatment with EP plus ICI, she developed immune-related myelitis with positive paraneoplastic autoantibodies (CV2, SOX1, ZIC4). Spinal MRI showed diffuse abnormal signal shadow in the cervicothoracic spinal cord. She was discontinued for chemotherapy, and treated with high-dose steroids, intravenous immunoglobulin and plasmapheresis, maintenance therapy with steroids resulted in a favorable neurologic outcome. This is the first report of durvalumab-related PNSs. We supposed that the development of paraneoplastic myelitis was causally related to immune activation by durvalumab. Prompt diagnosis and therapeutic intervention are essential for the effective treatment of paraneoplastic myelitis.
Keywords: Durvalumab; Immune checkpoint inhibitor; Immune-related adverse effects; Paraneoplastic neurologic syndromes; Programmed cell death ligand protein 1; Small-cell Lung cancer.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pujol JL, Greillier L, Audigier-Valette C, Moro-Sibilot D, Uwer L, Hureaux J, Guisier F, Carmier D, Madelaine J, Otto J, Gounant V, Merle P, Mourlanette P, Molinier O, Renault A, Rabeau A, Antoine M, Denis MG, Bommart S, Langlais A, Morin F, Souquet PJ. A Randomized Non-Comparative Phase II Study of Anti-programmed cell death-ligand 1 atezolizumab or chemotherapy as second-line therapy in patients with small cell lung cancer: Results from the IFCT-1603 Trial. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14(5):903–913. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.01.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ferrara R, Imbimbo M, Malouf R, Paget-Bailly S, Calais F, Marchal C, Westeel V (2020) Single or combined immune checkpoint inhibitors compared to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 12:CD013257 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

