Clinical outcomes of stereotactic magnetic resonance image-guided adaptive radiotherapy for primary and metastatic tumors in the abdomen and pelvis
- PMID: 34288538
- PMCID: PMC8419771
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.4139
Clinical outcomes of stereotactic magnetic resonance image-guided adaptive radiotherapy for primary and metastatic tumors in the abdomen and pelvis
Abstract
Purpose: Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) delivers ablative doses with excellent local control. However, implementing SBRT for abdominal and pelvic tumors has been limited by the risk for treatment-related gastrointestinal toxicity. MRI-guided radiotherapy may ameliorate these risks and increase the therapeutic ratio. We report the clinical outcomes of stereotactic MRI-guided adaptive radiotherapy (SMART) for primary and metastatic tumors in the abdomen and pelvis.
Methods: From November 2014 to August 2017, the first 106 consecutive patients with 121 tumors in the abdomen and pelvis were treated with SMART at a single institution. Of the cohort, 41.5%, 15.1%, and 43.4% had primary, locally recurrent, and oligometastatic tumors, respectively. SMART was delivered using a tri-cobalt-60 gantry with on-board 0.35 Tesla MRI with respiratory breath-hold and daily adaptive re-planning when anatomically necessary. A median of 40Gy in five fractions was prescribed. The Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v.4.03 was used to score treatment-related toxicities. Local control (LC), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) were estimated using Kaplan-Meier method.
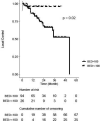
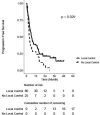
Results: Of the 510 treatments, seventy-one (13.9%) were adapted. Fatigue, nausea, and pain were the most common acute toxicities. 0.9 and 0% of patients experienced acute grade three and four toxicities, respectively. 5.2 and 2.1% of patients experienced late grade three and four toxicities, respectively. After a median follow-up of 20.4 months, the 2-year LC rate was 74% on a per-lesion basis. Two-year LC was 96% for lesions that were treated with BED10 ≥100 versus 69% for BED10 <100 (p = 0.02). PFS was significantly different between patients with and without locally controlled tumors (2-year PFS 21 vs. 8%, p = 0.03). Two-year OS was 57% for the entire cohort.
Conclusions: Favorable LC and PFS outcomes were observed with minimal morbidity for tumors in the abdomen and pelvis treated with SMART. Future prospective clinical trials to validate these findings are warranted.
Keywords: MR-guided radiation therapy; abdominal pelvic tumors; cancer management; stereotactic ablative radiotherapy; stereotactic body radiation therapy.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
MC: ViewRay, Inc.: personal fees. JL: ViewRay, Inc: grants, personal fees. NA: Varian, Inc.: personal fees; Brainlab: grants, personal fees, and non‐financial support. DL: ViewRay, Inc: co‐principal investigator of trial, consultant. AR: ViewRay, Inc: grants, personal fees. MS: ViewRay, Inc: personal fees. PL: ViewRay, Inc: clinical advisory board, honorarium, non‐financial support, co‐principal investigator of trial; Varian, Inc: consultant, honorarium, non‐financial support; AstraZeneca, Inc.: research grant, honorarium, non‐financial support. All other authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stereotactic Magnetic Resonance-Guided Daily Adaptive SABR (SMART) for Localised Non-Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer: First Reported Clinical Outcomes From the UK.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2024 Sep;36(9):576-584. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2024.05.012. Epub 2024 May 25. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2024. PMID: 38902119
-
Phase I trial of stereotactic MR-guided online adaptive radiation therapy (SMART) for the treatment of oligometastatic or unresectable primary malignancies of the abdomen.Radiother Oncol. 2018 Mar;126(3):519-526. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.11.032. Epub 2017 Dec 23. Radiother Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29277446 Clinical Trial.
-
Hypofractionated image-guided breath-hold SABR (stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy) of liver metastases--clinical results.Radiat Oncol. 2012 Jun 18;7:92. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-7-92. Radiat Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22710033 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic body radiotherapy for recurrent and oligometastatic soft tissue sarcoma.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Sep 29;20(1):322. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02781-1. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36171617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic outcome and related predictors of stereotactic body radiotherapy for small liver-confined HCC: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies.Radiat Oncol. 2021 Apr 8;16(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s13014-021-01761-1. Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33832536 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The impact of an Advanced Practice Radiation Therapist contouring for a CBCT-based adaptive radiotherapy program.Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2024 Mar 1;30:100242. doi: 10.1016/j.tipsro.2024.100242. eCollection 2024 Jun. Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38495830 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment planning for MR-guided SBRT of pancreatic tumors on a 1.5 T MR-Linac: A global consensus protocol.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2024 May 18;47:100797. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2024.100797. eCollection 2024 Jul. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38831754 Free PMC article.
-
Ventilation and perfusion MRI at a 0.35 T MR-Linac: feasibility and reproducibility study.Radiat Oncol. 2023 Apr 3;18(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13014-023-02244-1. Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37013541 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Applications of Magnetic Resonance-Guided Radiotherapy: A Narrative Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 26;15(11):2916. doi: 10.3390/cancers15112916. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37296879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical outcomes of patients with unresectable primary liver cancer treated with MR-guided stereotactic body radiation Therapy: A Six-Year experience.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023 Apr 19;41:100627. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2023.100627. eCollection 2023 Jul. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37441543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Timmerman RD, Kavanagh BD, Cho LC, Papiez L, Xing L. Stereotactic body radiation therapy in multiple organ sites. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(8):947–952. - PubMed
-
- Tse RV, Hawkins M, Lockwood G, et al. Phase I study of individualized stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(4):657–664. - PubMed