Transepithelial accelerated corneal crosslinking for keratoconus eyes with maximum keratometry values larger than 58 diopters
- PMID: 34288636
- PMCID: PMC8845528
- DOI: 10.1097/j.jcrs.0000000000000733
Transepithelial accelerated corneal crosslinking for keratoconus eyes with maximum keratometry values larger than 58 diopters
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of transepithelial accelerated corneal crosslinking (CXL) for advanced keratoconus eyes with maximum keratometry (Kmax) values >58 diopters (D).
Setting: Department of Ophthalmology, Eye and ENT Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China.
Design: Prospective parallel control study.
Methods: 41 keratoconus eyes from 41 patients (mean age, 21.93 ± 5.48 years) who underwent transepithelial accelerated CXL were included prospectively. The enrolled eyes were divided into 2 groups according to their Kmax values (Group A, Kmax ≥58.0 D; Group B, Kmax <58.0 D). The examinations including assessment of uncorrected distance visual acuity (UDVA), corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA), corneal topography, and corneal endothelial cell density count were conducted preoperatively, at 1 day, 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year postoperatively.
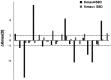
Results: All 41 eyes finished 1 year follow-up. No statistical difference was noted between the mean UDVA and CDVA in both groups throughout the follow-up duration. At 1-year postoperative follow-up, the CDVA increased by ≥2 lines in 45% (9/20) and 28.6% (6/21) eyes in Groups A and B, respectively. The mean preoperative Kmax in Groups A and B were 62.51 ± 3.34 D and 49.98 ± 4.32 D, respectively, and that at postoperative 1-year follow-up were 61.94 ± 4.11 D and 50.24 ± 4.72 D, respectively. The Kmax values of 30% (6/20) eyes in Group A and 4.8% (1/21) eyes in Group B decreased by more than 1 D. Deduction of flat K, steep K, mean K, and Kmax showed no significant difference between the 2 groups at 1-year postoperative follow-up. Moreover, 20% (4/20) and 23.8% (5/21) of eyes in Groups A and B, respectively, showed progress at postoperative 1-year follow-up.
Conclusions: Transepithelial accelerated CXL can safely treat advanced keratoconus eyes with Kmax values ≥58.0 D with some extent of efficacy and has similar progressive rate as Kmax values <58.0 D.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of ASCRS and ESCRS.
Figures
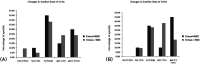

References
-
- Tuft SJ, Moodaley LC, Gregory WM, Davison CR, Buckley RJ. Prognostic factors for the progression of keratoconus. Ophthalmology 1994;101:439–447 - PubMed
-
- Wollensak G, Spoerl E, Seiler T. Riboflavin/ultraviolet-a-induced collagen crosslinking for the treatment of keratoconus. Am J Ophthalmol 2003;135:620–627 - PubMed
-
- Vinciguerra R, Romano MR, Camesasca FI, Azzolini C, Trazza S, Morenghi E, Vinciguerra P. Corneal cross-linking as a treatment for keratoconus: four-year morphologic and clinical outcomes with respect to patient age. Ophthalmology 2013;120:908–916 - PubMed
-
- Koller T, Mrochen M, Seiler T. Complication and failure rates after corneal crosslinking. J Cataract Refract Surg 2009;35:1358–1362 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

