Comparison of 6 SARS-CoV-2 Molecular Methods and Correlation With the Cycle Threshold Distribution in Clinical Specimens
- PMID: 34289054
- PMCID: PMC8436400
- DOI: 10.1093/jalm/jfab086
Comparison of 6 SARS-CoV-2 Molecular Methods and Correlation With the Cycle Threshold Distribution in Clinical Specimens
Abstract
Background: The detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in patient samples is of critical importance in the management of patients and monitoring transmission in the population. However, data on the analytical performance characteristics for detection of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical specimens between individual targets within the same platform, and among different analytical platforms, are limited.
Methods: Here we evaluated the performance of 6 different sample-to-answer SARS-CoV-2 detection methods-Roche cobas 6800, Cepheid GeneXpert, Diasorin Simplexa, Luminex Aries emergency use authorization (EUA), Luminex Aries research use only (RUO), and bioMérieux BioFire-in clinical specimens with a range of viral loads.
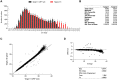
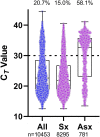
Results: The positive percentage agreement between the Roche cobas 6800 and GeneXpert was 100%, Diasorin 95%, Aries EUA 74%, Aries RUO 83%, and BioFire 97%. Notably, in samples with cycle threshold (Ct) values below 30 for the E gene on the Roche cobas 6800 platform, we found 100% positive agreement among all platforms. Given these results, we examined the distribution of over 10 000 Ct values of all positive specimens from individuals at our institution on the Roche cobas platform. Nearly 60% of specimens from asymptomatic individuals had a PCR Ct value >30 as measured using the cobas 6800 assay E gene.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate performance characteristics between different platforms by Ct value and provide data regarding the distribution of viral RNA present in positive specimens.
Keywords: COVID -19; PCR; SARS-CoV-2; diagnostics.
© American Association for Clinical Chemistry 2021. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection in asymptomatic populations using the DiaSorin molecular Simplexa and Roche Cobas EUA assays.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022 Jan;102(1):115513. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2021.115513. Epub 2021 Jul 31. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34649190 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical performance of Roche cobas 6800, Luminex ARIES, MiRXES Fortitude Kit 2.1, Altona RealStar, and Applied Biosystems TaqPath for SARS-CoV-2 detection in nasopharyngeal swabs.J Med Virol. 2021 Jul;93(7):4603-4607. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26940. Epub 2021 Mar 30. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 33719033 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Commercially Available and Laboratory-Developed Assays for In Vitro Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Clinical Laboratories.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Jul 23;58(8):e00821-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00821-20. Print 2020 Jul 23. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32350048 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Evaluation of the cobas SARS-CoV-2 Test and a Diagnostic Platform Switch during 48 Hours in the Midst of the COVID-19 Pandemic.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 May 26;58(6):e00599-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00599-20. Print 2020 May 26. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32277022 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding, Verifying, and Implementing Emergency Use Authorization Molecular Diagnostics for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Jul 23;58(8):e00796-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00796-20. Print 2020 Jul 23. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32381642 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of cycle-threshold-values between two commercial SARS-CoV-2 PCR assays.EXCLI J. 2023 Apr 4;22:397-399. doi: 10.17179/excli2023-5981. eCollection 2023. EXCLI J. 2023. PMID: 37346804 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Accuracy of point-of-care SARS-CoV-2 detection using buccal swabs in pediatric emergency departments.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Oct 29;12(12):e0188424. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01884-24. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39470284 Free PMC article.
-
Laboratory-based molecular test alternatives to RT-PCR for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 14;10(10):CD015618. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015618. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39400904
-
Isolation of SARS-CoV-2 in Viral Cell Culture in Immunocompromised Patients With Persistently Positive RT-PCR Results.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Feb 2;12:804175. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.804175. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35186791 Free PMC article.
-
Guidelines for COVID-19 Laboratory Testing for Emergency Departments From the New Diagnostic Technology Team of the Taiwan Society of Emergency Medicine.J Acute Med. 2022 Jun 1;12(2):45-52. doi: 10.6705/j.jacme.202206_12(2).0001. J Acute Med. 2022. PMID: 35860709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Long Q-X, Tang X-J, Shi Q-L, Li Q, Deng H-J, Yuan J, et al. Clinical and immunological assessment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat Med 2020;26:1200–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

