Immune mechanisms orchestrate tertiary lymphoid structures in tumors via cancer-associated fibroblasts
- PMID: 34289373
- PMCID: PMC8362934
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109422
Immune mechanisms orchestrate tertiary lymphoid structures in tumors via cancer-associated fibroblasts
Abstract
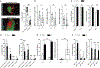
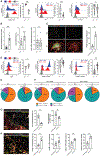
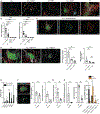
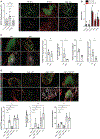
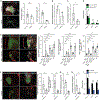
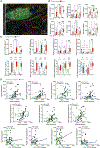
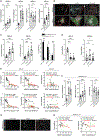
Tumor-associated tertiary lymphoid structures (TA-TLS) are associated with enhanced patient survival and responsiveness to cancer therapies, but the mechanisms underlying their development are unknown. We show here that TA-TLS development in murine melanoma is orchestrated by cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) with characteristics of lymphoid tissue organizer cells that are induced by tumor necrosis factor receptor signaling. CAF organization into reticular networks is mediated by CD8 T cells, while CAF accumulation and TA-TLS expansion depend on CXCL13-mediated recruitment of B cells expressing lymphotoxin-α1β2. Some of these elements are also overrepresented in human TA-TLS. Additionally, we demonstrate that immunotherapy induces more and larger TA-TLS that are more often organized with discrete T and B cell zones, and that TA-TLS presence, number, and size are correlated with reduced tumor size and overall response to checkpoint immunotherapy. This work provides a platform for manipulating TA-TLS development as a cancer immunotherapy strategy.
Keywords: B lymphocytes; B16 melanoma; CD8 T lymphocytes; cancer-associated fibroblasts; checkpoint blockade immunotherapy; lymphoid tissue inducer cell; lymphoid tissue organizer cell; lymphotoxin-β receptor; tertiary lymphoid structure; tumor necrosis factor receptor.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bombardieri M, Barone F, Humby F, Kelly S, McGurk M, Morgan P, Challacombe S, De Vita S, Valesini G, Spencer J, and Pitzalis C (2007). Activation-induced cytidine deaminase expression in follicular dendritic cell networks and interfollicular large B cells supports functionality of ectopic lymphoid neogenesis in autoimmune sialoadenitis and MALT lymphoma in Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Immunol 179, 4929–4938. - PubMed
-
- Browning JL, Allaire N, Ngam-Ek A, Notidis E, Hunt J, Perrin S, and Fava RA (2005). Lymphotoxin-beta receptor signaling is required for the homeostatic control of HEV differentiation and function. Immunity 23, 539–550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

