Exposure-safety analyses of nintedanib in patients with chronic fibrosing interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 34289823
- PMCID: PMC8293560
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-021-01598-0
Exposure-safety analyses of nintedanib in patients with chronic fibrosing interstitial lung disease
Abstract
Background: Nintedanib reduces the rate of decline in forced vital capacity in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), other chronic fibrosing interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) with a progressive phenotype and systemic sclerosis-associated ILD (SSc-ILD). The recommended dose of nintedanib is 150 mg twice daily (BID).
Methods: Data from Phase II and III trials in IPF and Phase III trials in SSc-ILD and progressive fibrosing ILDs other than IPF were analyzed to investigate the relationship between nintedanib plasma concentrations (exposure) and safety (liver enzyme elevations [defined as transaminase elevations equal or greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal] and diarrhea).
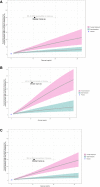
Results: Using data from 1403 subjects with IPF treated with 50-150 mg nintedanib BID, a parametric time-to-first-event model for liver enzyme elevations was established. Besides exposure, gender was a significant covariate, with a three-fourfold higher exposure-adjusted risk in females than males. Subsequent analysis of combined data from IPF, SSc-ILD (n = 576) and progressive fibrosing ILD (n = 663) studies suggested a consistent exposure-liver enzyme elevation relationship across studies. No exposure-diarrhea relationship was found using data from the various fibrosing ILDs, but diarrhea risk was dependent on dose administered.
Conclusions: The positive correlation between exposure and risk of liver enzyme elevations was consistent across nintedanib studies in IPF, SSc-ILD and progressing fibrosing ILDs other than IPF. The effect size does not warrant a priori dose adjustment in patients with altered plasma exposure (excluding hepatic impairment patients, where there are specific labelling recommendations). For diarrhea, dose administered was a better predictor than exposure.
Keywords: Exposure–safety relationship; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; Liver enzyme elevation; Nintedanib; Progressive fibrosing ILDs; Systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Ulrike Schmid, Benjamin Weber and Matthias Freiwald are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim. Support from Celine Sarr (Pharmetheus AB) was contracted and funded by Boehringer Ingelheim.
Figures
References
-
- European Medicines Agency: OFEV® (nintedanib): Summary of Product Characteristics. 2020. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/ofev-epar-pro.... Accessed 24 Sept 2020.
-
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration: OFEV® (nintedanib): prescribing information. 2020. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/205832s013lbl.pdf. Accessed 24 Sept 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

