Nuclear NAD+ homeostasis governed by NMNAT1 prevents apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells
- PMID: 34290089
- PMCID: PMC8294764
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abf3895
Nuclear NAD+ homeostasis governed by NMNAT1 prevents apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells
Abstract
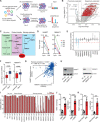
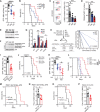
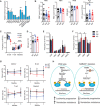
Metabolic dysregulation underlies malignant phenotypes attributed to cancer stem cells, such as unlimited proliferation and differentiation blockade. Here, we demonstrate that NAD+ metabolism enables acute myeloid leukemia (AML) to evade apoptosis, another hallmark of cancer stem cells. We integrated whole-genome CRISPR screening and pan-cancer genetic dependency mapping to identify NAMPT and NMNAT1 as AML dependencies governing NAD+ biosynthesis. While both NAMPT and NMNAT1 were required for AML, the presence of NAD+ precursors bypassed the dependence of AML on NAMPT but not NMNAT1, pointing to NMNAT1 as a gatekeeper of NAD+ biosynthesis. Deletion of NMNAT1 reduced nuclear NAD+, activated p53, and increased venetoclax sensitivity. Conversely, increased NAD+ biosynthesis promoted venetoclax resistance. Unlike leukemia stem cells (LSCs) in both murine and human AML xenograft models, NMNAT1 was dispensable for hematopoietic stem cells and hematopoiesis. Our findings identify NMNAT1 as a previously unidentified therapeutic target that maintains NAD+ for AML progression and chemoresistance.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures


References
-
- Ferrara F., Schiffer C. A., Acute myeloid leukaemia in adults. Lancet 381, 484–495 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Shlush L. I., Mitchell A., Heisler L., Abelson S., Ng S. W. K., Trotman-Grant A., Medeiros J. J. F., Rao-Bhatia A., Jaciw-Zurakowsky I., Marke R., McLeod J. L., Doedens M., Bader G., Voisin V., Xu C. J., McPherson J. D., Hudson T. J., Wang J. C. Y., Minden M. D., Dick J. E., Tracing the origins of relapse in acute myeloid leukaemia to stem cells. Nature 547, 104–108 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Lagadinou E. D., Sach A., Callahan K., Rossi R. M., Neering S. J., Minhajuddin M., Ashton J. M., Pei S., Grose V., O’Dwyer K. M., Liesveld J. L., Brookes P. S., Becker M. W., Jordan C. T., BCL-2 inhibition targets oxidative phosphorylation and selectively eradicates quiescent human leukemia stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 12, 329–341 (2013). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pei S., Minhajuddin M., Adane B., Khan N., Stevens B. M., Mack S. C., Lai S., Rich J. N., Inguva A., Shannon K. M., Kim H., Tan A. C., Myers J. R., Ashton J. M., Neff T., Pollyea D. A., Smith C. A., Jordan C. T., AMPK/FIS1-mediated mitophagy is required for self-renewal of human AML stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 23, 86–100.e6 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

