Process variations between Swiss units treating neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and their effect on short-term outcome
- PMID: 34290374
- PMCID: PMC8752440
- DOI: 10.1038/s41372-021-01156-w
Process variations between Swiss units treating neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and their effect on short-term outcome
Abstract
Objective: To compare therapeutic hypothermia (TH) treatment of term and near-term neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) between neonatal units.
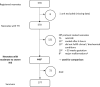
Study design: Population-based, retrospective analysis of TH initiation and maintenance, and of diagnostic imaging. The comparison between units was based on crude data analysis, indirect standardization, and adjusted logistic regression.
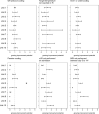
Results: TH was provided to 570 neonates with HIE between 2011 and 2018 in 10 Swiss units. We excluded 121 off-protocol cooled neonates to avoid selection bias. Of the remaining 449 neonates, the outcome was favorable to international benchmarks, but there were large unit-to-unit variations in baseline perinatal data and TH management. A total of 5% neonates did not reach target temperature within 7 h (3-10% between units), and 29% experienced over- or undercooling (0-38%).
Conclusion: Although the neonates had favorable short-term outcomes, areas for improvement remain for Swiss units in both process and outcome measures.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MA receives a salary as network coordinator for SwissNeoNet, the host of the National Asphyxia and Cooling Register. The remaining authors have no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Azzopardi DV, Strohm B, Edwards AD, Dyet L, Halliday HL, Juszczak E, et al. Moderate hypothermia to treat perinatal asphyxial encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1349–58. 10.1056/NEJMoa0900854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

