QPX7728, An Ultra-Broad-Spectrum B-Lactamase Inhibitor for Intravenous and Oral Therapy: Overview of Biochemical and Microbiological Characteristics
- PMID: 34290688
- PMCID: PMC8287861
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.697180
QPX7728, An Ultra-Broad-Spectrum B-Lactamase Inhibitor for Intravenous and Oral Therapy: Overview of Biochemical and Microbiological Characteristics
Abstract
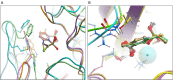
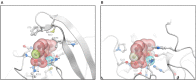
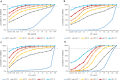
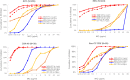
QPX7728 is a novel β-lactamase inhibitor (BLI) that belongs to a class of cyclic boronates. The first member of this class, vaborbactam, is a BLI in the recently approved Vabomere (meropenem-vaborbactam). In this paper we provide the overview of the biochemical, structural and microbiological studies that were recently conducted with QPX7728. We show that QPX7728 is an ultra-broad-spectrum β-lactamase inhibitor with the broadest spectrum of inhibition reported to date in a single BLI molecule; in addition to potent inhibition of clinically important serine β-lactamases, including Class A and D carbapenemases from Enterobacterales and notably, diverse Class D carbapenemases from Acinetobacter, it also inhibits many metallo β-lactamases. Importantly, it is minimally affected by general intrinsic resistance mechanisms such as efflux and porin mutations that impede entry of drugs into gram-negative bacteria. QPX7728 combinations with several intravenous (IV) β-lactam antibiotics shows broad coverage of Enterobacterales, Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, including strains that are resistant to other IV β-lactam-BLI combinations, e.g., ceftazidime-avibactam, ceftolozane-tazobactam, meropenem-vaborbactam and imipenem-relebactam that were recently approved for clinical use. Based on studies with P. aeruginosa, different partner β-lactams in combination with QPX7728 may be optimal for the coverage of susceptible organisms. This provides microbiological justification for a stand-alone BLI product for co-administration with different β-lactams. QPX7728 can also be delivered orally; thus, its ultra-broad β-lactamase inhibition spectrum and other features could be also applied to oral QPX7728-based combination products. Clinical development of QPX7728 has been initiated.
Keywords: Acinetobacter; CRE; Pseudomonas; QPX7728; beta-lactamase inhibitor; carbapenemase; metallo β-lactamase.
Copyright © 2021 Lomovskaya, Tsivkovski, Sun, Reddy, Totrov, Hecker, Griffith, Loutit and Dudley.
Conflict of interest statement
OL, RT, DS, RR, SH, DG, JL, and MD are employees and shareholders of Qpex Biopharma that is developing QPX7728. MT is an employee of Molsoft, LLC. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Barnes M. D., Winkler M. L., Taracila M. A., Page M. G., Desarbre E., Kreiswirth B. N., et al. (2017). Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-2 (KPC-2), substitutions at ambler position Asp179, and resistance to ceftazidime-avibactam: unique antibiotic-resistant phenotypes emerge from beta-lactamase protein engineering. MBio 8 e00528–17. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Castanheira M., Doyle T. B., Smith C. J., Mendes R. E., Sader H. S. (2019). Combination of MexAB-OprM overexpression and mutations in efflux regulators, PBPs and chaperone proteins is responsible for ceftazidime/avibactam resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates from US hospitals. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 74 2588–2595. 10.1093/jac/dkz243 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

