Lectin Pathway Mediates Complement Activation by SARS-CoV-2 Proteins
- PMID: 34290717
- PMCID: PMC8287855
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.714511
Lectin Pathway Mediates Complement Activation by SARS-CoV-2 Proteins
Abstract
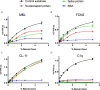
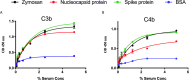
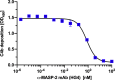
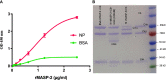
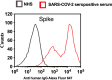
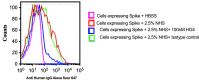
Early and persistent activation of complement is considered to play a key role in the pathogenesis of COVID-19. Complement activation products orchestrate a proinflammatory environment that might be critical for the induction and maintenance of a severe inflammatory response to SARS-CoV-2 by recruiting cells of the cellular immune system to the sites of infection and shifting their state of activation towards an inflammatory phenotype. It precedes pathophysiological milestone events like the cytokine storm, progressive endothelial injury triggering microangiopathy, and further complement activation, and causes an acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). To date, the application of antiviral drugs and corticosteroids have shown efficacy in the early stages of SARS-CoV-2 infection, but failed to ameliorate disease severity in patients who progressed to severe COVID-19 pathology. This report demonstrates that lectin pathway (LP) recognition molecules of the complement system, such as MBL, FCN-2 and CL-11, bind to SARS-CoV-2 S- and N-proteins, with subsequent activation of LP-mediated C3b and C4b deposition. In addition, our results confirm and underline that the N-protein of SARS-CoV-2 binds directly to the LP- effector enzyme MASP-2 and activates complement. Inhibition of the LP using an inhibitory monoclonal antibody against MASP-2 effectively blocks LP-mediated complement activation. FACS analyses using transfected HEK-293 cells expressing SARS-CoV-2 S protein confirm a robust LP-dependent C3b deposition on the cell surface which is inhibited by the MASP-2 inhibitory antibody. In light of our present results, and the encouraging performance of our clinical candidate MASP-2 inhibitor Narsoplimab in recently published clinical trials, we suggest that the targeting of MASP-2 provides an unsurpassed window of therapeutic efficacy for the treatment of severe COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; complement system; innate immunity; lectin pathway.
Copyright © 2021 Ali, Ferrari, Lynch, Yaseen, Dudler, Gragerov, Demopulos, Heeney and Schwaeble.
Conflict of interest statement
WS, NL, and YA are consultants to Omeros Inc., which is developing inhibitors of the lectin pathway. GD, TD, SG, and SY are employed by Omeros Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

