Calcium Solubilization Ability and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Hydrolyzed Casein
- PMID: 34291216
- PMCID: PMC8277184
- DOI: 10.5851/kosfa.2021.e29
Calcium Solubilization Ability and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Hydrolyzed Casein
Abstract
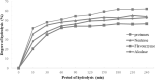
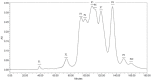
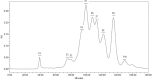
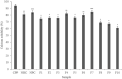
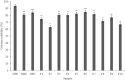
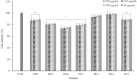
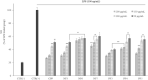
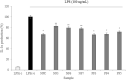
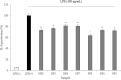
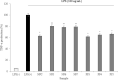
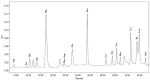
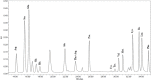
This study performed to evaluate the applicability of functional dairy food materials by comparing the calcium solubilization ability and anti-inflammatory effects of hydrolyzed casein protein. Commercial enzyme (Alcalase®; Neutrase®; Protamex®; Flavourzyme®) was added to the 10% casein solution to prepare the casein hydrolysates. Samples obtained every hour [1:200 (w/v)]. According to results of measuring the degree of hydrolysis (DH), all of four enzymatic hydrolysates increased rapidly from 30 to 40 min, and after 150 min, there were no change. Protamex® and Neutrase® had the highest DH compared to others enzymatic hydrolysates. After that, peptides obtained throughout a preparative liquid chromatography system. In the calcium solubility experiments, neutrase fraction (NF) 4 and NF7 showed similar activities with casein phosphopeptide (CPP). In vitro cell experiments showed that no cytotoxicity except for NF6. Also, the production of nitric oxide (NO) inhibited as the concentration of fraction samples increased. The cytokine (IL-1α, IL-6, and TNF-α) production was lower than lipopolysaccharide (+) group significantly. Therefore, the possibility of anti-inflammatory activity found in the hydrolyzed samples. According to the above experiments, NF3 and Protamex Fraction (PF) 3 selected. Amino acids selected throughout an AccQ-Tag system. As a result, 17 species of amino acids and several species of unknown amino acids identified. Both fractions had the highest content of phenylalanine. This study identified the potential of biologically active and functional peptides derived from casein that affect the food and dairy industry.
Keywords: amino acids; anti-inflammatory effects; calcium solubilization ability; casein; milk protein.
© Korean Society for Food Science of Animal Resources.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of bitterness in enzymatic hydrolysates of soy protein isolate by taste dilution analysis.J Food Sci. 2008 Jan;73(1):S41-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00610.x. J Food Sci. 2008. PMID: 18211368
-
Influence of enzymatic hydrolysis and enzyme type on the nutritional and antioxidant properties of pumpkin meal hydrolysates.Food Funct. 2013 Apr 30;4(5):811-20. doi: 10.1039/c3fo30347k. Food Funct. 2013. PMID: 23591974
-
Enzymatic hydrolysis of heated whey: iron-binding ability of peptides and antigenic protein fractions.J Dairy Sci. 2007 Sep;90(9):4033-42. doi: 10.3168/jds.2007-0228. J Dairy Sci. 2007. PMID: 17699019
-
Antioxidant Effect and Functional Properties of Hydrolysates Derived from Egg-White Protein.Korean J Food Sci Anim Resour. 2014;34(3):362-71. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2014.34.3.362. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Korean J Food Sci Anim Resour. 2014. PMID: 26761178 Free PMC article.
-
Yak milk casein as a functional ingredient: preparation and identification of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides.J Dairy Res. 2007 Feb;74(1):18-25. doi: 10.1017/S0022029906002056. Epub 2006 Sep 21. J Dairy Res. 2007. PMID: 16987434
Cited by
-
In vitro assessment of the probiotic properties of an industrial preparation containing Lacticaseibacillus paracasei in the context of athlete health.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 9;13:857987. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.857987. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36016576 Free PMC article.
-
Functional proteins in breast milk and their correlation with the development of the infant gut microbiota: a study of mother-infant pairs.Front Microbiol. 2023 Sep 13;14:1239501. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1239501. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37771701 Free PMC article.
-
Preventative and therapeutic potential of animal milk components against COVID-19: A comprehensive review.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Mar 23;11(6):2547-2579. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3314. eCollection 2023 Jun. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37324885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler-Nissen J. Enzymic hydrolysis of food proteins. Elsevier; London, UK: 1986.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

