Evaluation of serum calcium differences in hypertensive crises and control patients: A randomly matched case-control study
- PMID: 34291559
- PMCID: PMC8635273
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.14268
Evaluation of serum calcium differences in hypertensive crises and control patients: A randomly matched case-control study
Abstract
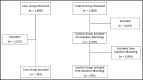
The role of calcium in blood pressure has been widely studied among hypertensive patients; however, no study has explored the role of calcium in hypertensive crises. The primary objective of this study is to evaluate the differences in serum calcium levels between hypertensive crises patients and a 1:1 random matched controls (age-, sex-, race-, diabetes, and body mass index matched). This study is a single-center, retrospective, chart review, case-control study of patients with hypertensive crises (case group) and patients without hypertensive crises (control group). Patients were included in the case group if they were 18 years of age or older with hypertensive crises and have a documented calcium level. The control group patients were required to be 18 years of age or older, have a documented calcium level, and have no diagnosis of hypertensive crises. The primary outcome of the study was to compare the mean serum calcium in patients with hypertensive crises vs patients without hypertensive crises. Five hundred and sixty-six patients were included in the study: 283 patients in both the case group and control group. The primary outcome results showed that serum calcium concentration was not significantly different between the case group (8.99 ± 0.78 mg/dL) and control group (8.96 ± 0.75 mg/dL) (P = .606). This study found no significant difference in serum calcium levels in patients with hypertensive crises compared to a random matched control group. Larger observational or experimental studies may be useful to evaluate the effect of calcium on blood pressure in hypertensive crises.
Keywords: calcium; hypertension-general; hypertensive crises; magnesium; phosphorus.
© 2021 The Authors. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(19):e127‐e248. 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.11.006 - DOI - PubMed
-
- National High Blood Pressure Education Program . The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (US); 2004. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9630/. Accessed March 19, 2020. - PubMed
-
- Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Eur Heart J. 2018;39(33):3021‐3104. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical