Venetoclax enhances T cell-mediated antileukemic activity by increasing ROS production
- PMID: 34292323
- PMCID: PMC8310428
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2020009081
Venetoclax enhances T cell-mediated antileukemic activity by increasing ROS production
Erratum in
-
Lee JB, Khan DH, Hurren R, et al. Venetoclax enhances T cell-mediated antileukemic activity by increasing ROS production. Blood. 2021;138(3):234-245.Blood. 2023 Mar 23;141(12):1495. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023019985. Blood. 2023. PMID: 36951880 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
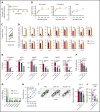
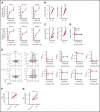
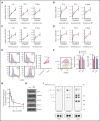
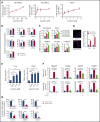
Venetoclax, a Bcl-2 inhibitor, in combination with the hypomethylating agent azacytidine, achieves complete remission with or without count recovery in ∼70% of treatment-naive elderly patients unfit for conventional intensive chemotherapy. However, the mechanism of action of this drug combination is not fully understood. We discovered that venetoclax directly activated T cells to increase their cytotoxicity against acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in vitro and in vivo. Venetoclax enhanced T-cell effector function by increasing reactive oxygen species generation through inhibition of respiratory chain supercomplexes formation. In addition, azacytidine induced a viral mimicry response in AML cells by activating the STING/cGAS pathway, thereby rendering the AML cells more susceptible to T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Similar findings were seen in patients treated with venetoclax, as this treatment increased reactive oxygen species generation and activated T cells. Collectively, this study presents a new immune-mediated mechanism of action for venetoclax and azacytidine in the treatment of AML and highlights a potential combination of venetoclax and adoptive cell therapy for patients with AML.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures

References
-
- Lee JB, Chen B, Vasic D, Law AD, Zhang L. Cellular immunotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia: How specific should it be? Blood Rev. 2019;35:18-31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

