Antibody status and cumulative incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among adults in three regions of France following the first lockdown and associated risk factors: a multicohort study
- PMID: 34293141
- PMCID: PMC8344948
- DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyab110
Antibody status and cumulative incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among adults in three regions of France following the first lockdown and associated risk factors: a multicohort study
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: Antibody status and cumulative incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among adults in three regions of France following the first lockdown and associated risk factors: a multicohort study.Int J Epidemiol. 2021 Nov 10;50(5):1755. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyab173. Int J Epidemiol. 2021. PMID: 34453524 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: We aimed to estimate the seropositivity to anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in May-June 2020 after the first lockdown period in adults living in three regions in France and to identify the associated risk factors.
Methods: Between 4 May 2020 and 23 June 2020, 16 000 participants in a survey on COVID-19 from an existing consortium of three general adult population cohorts living in the Ile-de-France (IDF) or Grand Est (GE) (two regions with high rate of COVID-19) or in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine (NA) (with a low rate) were randomly selected to take a dried-blood spot for anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies assessment with three different serological methods (ClinicalTrial Identifier #NCT04392388). The primary outcome was a positive anti-SARS-CoV-2 ELISA IgG result against the spike protein of the virus (ELISA-S). Estimates were adjusted using sampling weights and post-stratification methods. Multiple imputation was used to infer the cumulative incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection with adjustments for imperfect tests accuracies.
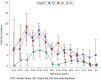
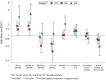
Results: The analysis included 14 628 participants, 983 with a positive ELISA-S. The weighted estimates of seropositivity and cumulative incidence were 10.0% [95% confidence interval (CI): 9.1%, 10.9%] and 11.4% (95% CI: 10.1%, 12.8%) in IDF, 9.0% (95% CI: 7.7%, 10.2%) and 9.8% (95% CI: 8.1%, 11.8%) in GE and 3.1% (95% CI: 2.4%, 3.7%) and 2.9% (95% CI: 2.1%, 3.8%) in NA, respectively. Seropositivity was higher in younger participants [odds ratio (OR) = 1.84 (95% CI: 1.79, 6.09) in <40 vs 50-60 years old and OR = 0.56 (95% CI: 0.42, 0.74) in ≥70 vs 50-60 years old)] and when at least one child or adolescent lived in the same household [OR = 1.30 (95% CI: 1.11, 1.53)] and was lower in smokers compared with non-smokers [OR = 0.71 (95% CI: 0.57, 0.89)].
Conclusions: Seropositivity to anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in the French adult population was ≤10% after the first wave. Modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors were identified.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; cohort; general population; risk factors; seroprevalence.
© The Author(s) 2021; all rights reserved. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Epidemiological Association.
Figures

References
-
- Koopmans M, Haagmans B. Assessing the extent of SARS-CoV-2 circulation through serological studies. Nat Med 2020;26:1171–72. - PubMed
-
- Bobrovitz N, Aro ra RK, Cao C et al. Global seroprevalence of SARS-SoV-2 antibodies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. medRxiv 2020; doi:10.1101/2020.11.17.20233460, 18 November preprint: not peer-reviewed.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- #ANR-20-COVI-000, #ANR-10-COHO-06/Agence Nationale de la Recherche
- Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale [#20RR052-00], Inserm (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale) [#C20-26]
- #ANR-20-COVI-000/ANR (Agence Nationale de la Recherche)
- #20RR052-00/Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale
- Inserm (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale) [#C20-26]
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

