Bridging neuronal correlations and dimensionality reduction
- PMID: 34293295
- PMCID: PMC8505167
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.06.028
Bridging neuronal correlations and dimensionality reduction
Abstract
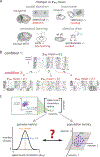
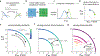
Two commonly used approaches to study interactions among neurons are spike count correlation, which describes pairs of neurons, and dimensionality reduction, applied to a population of neurons. Although both approaches have been used to study trial-to-trial neuronal variability correlated among neurons, they are often used in isolation and have not been directly related. We first established concrete mathematical and empirical relationships between pairwise correlation and metrics of population-wide covariability based on dimensionality reduction. Applying these insights to macaque V4 population recordings, we found that the previously reported decrease in mean pairwise correlation associated with attention stemmed from three distinct changes in population-wide covariability. Overall, our work builds the intuition and formalism to bridge between pairwise correlation and population-wide covariability and presents a cautionary tale about the inferences one can make about population activity by using a single statistic, whether it be mean pairwise correlation or dimensionality.
Keywords: dimensionality reduction; neuronal population; spatial attention; spike count correlation; visual area V4.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

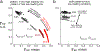


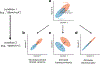
References
-
- Abbott LF, and Dayan P. (1999). The effect of correlated variability on the accuracy of a population code. Neural Comput. 11, 91–101. - PubMed
-
- Ahrens MB, Orger MB, Robson DN, Li JM, and Keller PJ (2013). Whole-brain functional imaging at cellular resolution using light-sheet microscopy. Nat. Methods 10, 413–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

