The influential factors for achieving universal health coverage in Iran: a multimethod study
- PMID: 34294100
- PMCID: PMC8299681
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-021-06673-0
The influential factors for achieving universal health coverage in Iran: a multimethod study
Abstract
Background: The initial purpose of healthcare systems around the world is to promote and maintain the health of the population. Universal Health Coverage (UHC) is a new approach by which a healthcare system can reach its goals. World Health Organization (WHO) emphasized maximum population coverage, health service coverage, and financial protection, as three dimensions of UHC. In progress for achieving UHC, recognizing the influential factors allows us to accelerate such progress. Therefore, this study aimed to identify the influential factors to achieve UHC in Iran.
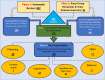
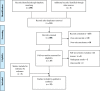
Methods: This is a multi-method study was conducted in four phases: First, a systematic review of the literature was conducted to identify the factors in PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Scopus, ProQuest, Cochrane library, and Science Direct databases, and hand searching google scholar search engine. For recognizing the unmentioned factors, a qualitative study consisting of one session of Focus Group Discussion (FGD) and five semi-structured interviews with experts was designed. The extracted factors were merged and categorized by round table discussion. Finally, the pre-categorized factors were refined and re-categorized under the health system's control knobs framework during three expert panel sessions.
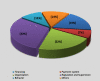
Results: Finally, 33 studies were included. Eight hundred two factors were extracted through systematic review and 96 factors through FGD and interviews (totally, 898). After refining them by the experts' panel, 105 factors were categorized within the control knob framework (financing 19, payment system7, Organization 23, regulation and supervision 33, Behavior 11, and Others 12). The majority of the identified factors were related to the "regulation and supervision" dimension, whilst the "payment system" entailed the fewest. The political commitment during political turmoil, excessive attention to the treatment, referral system, paying out of pocket(OOP) and protection against high costs, economic growth, sanctions, conflict of interests, weakness of the information system, prioritization of services, health system fragmented, lack of managerial support and lack of standard benefits packages were identified as the leading factors on the way to UHC.
Conclusion: Considering the distinctive role of the context in policymaking, the identification of the factors affecting UHC accompanying by the countries' experiences about UHC, can boost our speed toward it. Moreover, adopting a long-term plan toward UHC based on these factors and the robust implementation of it pave the way for Iran to achieve better outcomes comparing to their efforts.
Keywords: Control knobs; Health system; Influential factors; Iran; Systematic review; Universal health coverage.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state they have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Universality of universal health coverage: A scoping review.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 22;17(8):e0269507. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269507. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35994455 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing progress in the national health financing system towards universal health coverage in Iran: a mixed-method study protocol.Health Res Policy Syst. 2021 Jan 12;19(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12961-020-00610-z. Health Res Policy Syst. 2021. PMID: 33435989 Free PMC article.
-
Universal health coverage under the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action's sanctions: strategic purchasing approach in the Iranian health system.Health Promot Int. 2021 Aug 24;36(3):693-702. doi: 10.1093/heapro/daaa070. Health Promot Int. 2021. PMID: 33006610
-
Qualitative analysis of Iranian sixth five-year economic, social, and cultural development plan from universal health coverage perspective.BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Sep 14;21(1):966. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-06985-1. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. PMID: 34521388 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and Opportunities of Universal Health Coverage in Africa: A Scoping Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 Jan 10;22(1):86. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22010086. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39857539 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Challenges and Weaknesses of Leadership and Governance-related Health Policies in Iran: A Systematic Review.Arch Iran Med. 2024 Sep 1;27(9):508-521. doi: 10.34172/aim.28907. Epub 2024 Sep 1. Arch Iran Med. 2024. PMID: 39465526 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring hospitals' functional preparedness effective factors in response to disasters: a qualitative study in a lower middle-income country.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Feb 13;24(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-10630-y. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 38350908 Free PMC article.
-
Towards universal health coverage: The level and determinants of enrollment in the Community-Based Health Insurance (CBHI) scheme in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 18;17(8):e0272959. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272959. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35980888 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Influencing Paternalistic Clinical Environment in Iran: An Exploratory Research Brief.J Patient Exp. 2025 May 30;12:23743735251346665. doi: 10.1177/23743735251346665. eCollection 2025. J Patient Exp. 2025. PMID: 40453107 Free PMC article.
-
Universality of universal health coverage: A scoping review.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 22;17(8):e0269507. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269507. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35994455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Evans DB, Saksena P, Elovainio R, Boerma T. Measuring progress towards universal coverage. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012.
-
- Organization WH. The world health report 2000: health systems: improving performance: World Health Organization; 2000.
-
- Maeda A, Araujo E, Cashin C, Harris J, Ikegami N, Reich MR. Universal health coverage for inclusive and sustainable development: a synthesis of 11 country case studies: World Bank publications; 2014.
-
- Xu Y, Huang C, Colón-Ramos U: Moving toward universal health coverage (UHC) to achieve inclusive and sustainable health development: three essential strategies drawn from Asian experience: comment on’Improving the World’s health through the Post-2015 development agenda: perspectives from Rwanda’. 2015. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

