Vulnerability of the North Water ecosystem to climate change
- PMID: 34294719
- PMCID: PMC8298575
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-24742-0
Vulnerability of the North Water ecosystem to climate change
Abstract
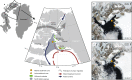
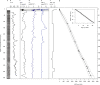
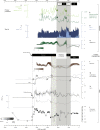
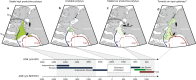
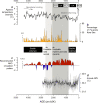
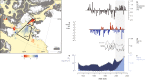
High Arctic ecosystems and Indigenous livelihoods are tightly linked and exposed to climate change, yet assessing their sensitivity requires a long-term perspective. Here, we assess the vulnerability of the North Water polynya, a unique seaice ecosystem that sustains the world's northernmost Inuit communities and several keystone Arctic species. We reconstruct mid-to-late Holocene changes in sea ice, marine primary production, and little auk colony dynamics through multi-proxy analysis of marine and lake sediment cores. Our results suggest a productive ecosystem by 4400-4200 cal yrs b2k coincident with the arrival of the first humans in Greenland. Climate forcing during the late Holocene, leading to periods of polynya instability and marine productivity decline, is strikingly coeval with the human abandonment of Greenland from c. 2200-1200 cal yrs b2k. Our long-term perspective highlights the future decline of the North Water ecosystem, due to climate warming and changing sea-ice conditions, as an important climate change risk.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- IPCC AR5 WG2. IPPC’s Fifth Assessment Report: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (IPCC WG2, 2014).
-
- Grønnow, B. & Sørensen, M. Palaeo-Eskimo migrations into Greenland: The Canadian Connection. In Dynamics of Northern Societies. Proceedings of the SILA/NABO Conference on Arctic and North Atlantic Archaeology, Copenhagen (eds Arneborg, J. & Grønnow, B.) 59–74 (National Museum, Studies in Archaeology & History, 2006).
-
- Marchese C, et al. Changes in phytoplankton bloom phenology over the North Water (NOW) polynya: a response to changing environmental conditions. Polar Biol. 2017;40:1721–1737. doi: 10.1007/s00300-017-2095-2. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

