Measurement of Cortical Atrophy and Its Correlation to Memory Impairment in Patients With Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis Based on VBM-DARTEL
- PMID: 34295237
- PMCID: PMC8289738
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.620763
Measurement of Cortical Atrophy and Its Correlation to Memory Impairment in Patients With Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis Based on VBM-DARTEL
Abstract
Objective: Severe carotid artery stenosis (CAS) can lead to atrophy of gray matter (GM) and memory impairment; however, the underlying mechanism is unknown. Thus, we aimed to identify memory impairment and GM atrophy and explore the possible correlation between them in patients with asymptomatic severe CAS.
Methods: Twenty-four patients with asymptomatic severe CAS and 10 healthy controls completed the mini-mental state examination (MMSE) and clinical memory scale (CMS) and underwent 7T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. Field intensity inhomogeneities were corrected. Images were processed using VBM8, and GM images were flipped. First, 11 flipped and 10 non-flipped images of patients with unilateral CAS and 5 flipped and 5 non-flipped images of controls were pre-processed using DARTEL algorithm and analyzed using an analysis of variance (ANOVA). Second, flipped and non-flipped images of unilateral patients were similarly pre-processed and analyzed using the paired t-test. Third, pre-processed non-flipped GM images and CMS scores of 24 patients were analyzed by multiple regression analysis. Nuisance variables were corrected accordingly.
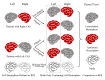
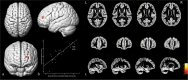
Results: Basic information was well matched between patients and controls. MMSE scores of patients were in the normal range; however, memory function was significantly reduced (all P < 0.05). GM volumes of patients were significantly reduced in the anterior circulation regions. The stenosis-side hemispheres showed greater atrophy. GM volumes of the left pars opercularis, pars triangularis, and middle frontal gyrus were strongly positively correlated with the total scores of CMS (all r > 0.7, P = 0.001). Additionally, the left middle frontal gyrus was strongly positively correlated with associative memory (r = 0.853, P = 0.001). The left pars opercularis was moderately positively correlated with semantic memory (r = 0.695, P = 0.001).
Conclusion: Patients with asymptomatic CAS suffer from memory impairment. Bilateral anterior circulation regions showed extensive atrophy. The hemisphere with stenosis showed severer atrophy. Memory impairment in patients may be related to atrophy of the left frontal gyrus and atrophy of different regions may result in different memory impairments.
Keywords: 7T-MRI; VBM analysis; asymptomatic carotid stenosis; cerebral gray matter atrophy; memory deficiency.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Cai, Luo, Zhang, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Examination of brain area volumes based on voxel-based morphometry and multidomain cognitive impairment in asymptomatic unilateral carotid artery stenosis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Mar 15;15:1128380. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1128380. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37009454 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Carotid Artery Stenting on Cerebral Perfusion, Functional Connectivity, and Cognition in Severe Asymptomatic Carotid Stenosis Patients.Front Neurol. 2017 Aug 9;8:403. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00403. eCollection 2017. Front Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28848495 Free PMC article.
-
Progression of gray matter atrophy in seizure-free patients with temporal lobe epilepsy.Epilepsia. 2016 Apr;57(4):621-9. doi: 10.1111/epi.13334. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Epilepsia. 2016. PMID: 26865066
-
Changes of brain structure in Parkinson's disease patients with mild cognitive impairment analyzed via VBM technology.Neurosci Lett. 2017 Sep 29;658:121-132. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.08.028. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Neurosci Lett. 2017. PMID: 28823894
-
Voxelwise meta-analysis of gray matter anomalies in Parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy and Parkinson's disease using anatomic likelihood estimation.Neurosci Lett. 2015 Feb 5;587:79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.12.007. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Neurosci Lett. 2015. PMID: 25484255
Cited by
-
Neuroimaging anomalies in asymptomatic middle cerebral artery steno-occlusive disease with normal-appearing white matter.Front Neurol. 2023 Aug 24;14:1206786. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1206786. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37693758 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in brain morphology and functional connectivity mediate cognitive decline in carotid atherosclerotic stenosis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Jun 20;16:1395911. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1395911. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38974904 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of medial temporal and parietal atrophy on cognitive function in dementia.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 4;14(1):5281. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56023-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38438548 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive and sensitive MRI assessment of radiation-induced cognitive dysfunction via voxel-based morphological and functional connectivity.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025 Aug 21;13(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s40478-025-02092-y. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025. PMID: 40841911 Free PMC article.
-
Examination of brain area volumes based on voxel-based morphometry and multidomain cognitive impairment in asymptomatic unilateral carotid artery stenosis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Mar 15;15:1128380. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1128380. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37009454 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

