Low Growth Hormone Levels Predict Poor Outcome of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure
- PMID: 34295909
- PMCID: PMC8290074
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.655863
Low Growth Hormone Levels Predict Poor Outcome of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure
Abstract
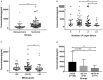
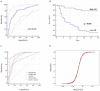
Background and Aims: Hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure (HBV-ACLF) remains a serious entity with high mortality. Growth hormone (GH) is related to the liver metabolism and regeneration. The present study aimed to explore the changes and prognostic efficacy of GH on the outcome of HBV-ACLF. Methods: A prospective cohort of 124 patients and a cross-sectional cohort of 142 subjects were enrolled. GH and insulin-like growth factor-1(IGF-1) were detected by ELISA. Thirty-day survival was collected and the association between GH and the 30-day mortality of HBV-ACLF was analyzed. Results: The mean age of the whole prospective cohort was 46.61 ± 12.71 years, and 19 (15.3%) patients were female. The median (IQR) of GH levels in non-survivors were 1106.55 (674.25, 1922.4) pg/ml, which were significantly lower than in survivors (p < 0.001). In the cross-sectional cohort, GH level was significantly higher in liver cirrhosis - acute decompensation (LC-AD) group than liver cirrhosis (LC) group (p < 0.001) while IGF-1 decreased significantly in LC, LC-AD, ACLF groups than health control (HC) and chronic Hepatitis B (CHB) groups (p < 0.001). The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of GH for predicting 30-day mortality was 0.793. We built a new prognostic model, namely MELD-GH, which showed better predictive efficacy than Child-Pugh, MELD, CLIF-SOFA, and CLIF-C ACLF scores. Conclusions: Low GH predicted the poor outcome of HBV-ACLF patients. GH and IGF-1 levels were differently distributed among HC, CHB, LC, LC-AD, and ACLF patients. MELD-GH had better predictive accuracy when compared to Child-Pugh, MELD, CLIF-SOFA, and CLIF-C ACLF scores.
Keywords: acute-on-chronic liver failure; growth hormone; hepatitis B; mortality; prognostic model.
Copyright © 2021 Wu, Zhang, Ma, Zhao, Chen, Zhang, Liu, Xu and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chronic liver failure-consortium acute-on-chronic liver failure and acute decompensation scores predict mortality in Brazilian cirrhotic patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Jul 28;23(28):5237-5245. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5237. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28811718 Free PMC article.
-
HINT: a novel prognostic model for patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Oct;48(7):750-760. doi: 10.1111/apt.14927. Epub 2018 Aug 1. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30069888
-
Validation of prognostic scores to predict short-term mortality in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure: The CLIF-C OF is superior to MELD, CLIF SOFA, and CLIF-C ACLF.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Apr;96(17):e6802. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006802. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28445322 Free PMC article.
-
[Study on the application value of MELD-Na, CLIF-C OFs, COSSH-ACLFs and NLR scoring systems in patients with hepatitis B virus related acute-on-chronic liver failure].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Dec;32(12):1496-1501. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200720-00536. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 33541504 Chinese.
-
Artificial neural network-based models used for predicting 28- and 90-day mortality of patients with hepatitis B-associated acute-on-chronic liver failure.BMC Gastroenterol. 2020 Mar 13;20(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01191-5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32188419 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of key genes and infiltrating immune cells among acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure and HBV-associated acute liver failure.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Jul;10(14):775. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-2742. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35965803 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and molecular docking verification of feature genes related to phospholipid metabolism in hepatocarcinoma caused by hepatitis B.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Aug 24;23(1):268. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02253-3. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39182089 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Novel Prognostic Nomogram for High Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Score Recipients Following Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 3;9:772048. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.772048. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35308496 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

