Fostering reproducibility, reusability, and technology transfer in health informatics
- PMID: 34296072
- PMCID: PMC8282945
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102803
Fostering reproducibility, reusability, and technology transfer in health informatics
Abstract
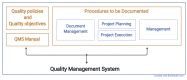
Computational methods can transform healthcare. In particular, health informatics with artificial intelligence has shown tremendous potential when applied in various fields of medical research and has opened a new era for precision medicine. The development of reusable biomedical software for research or clinical practice is time-consuming and requires rigorous compliance with quality requirements as defined by international standards. However, research projects rarely implement such measures, hindering smooth technology transfer into the research community or manufacturers as well as reproducibility and reusability. Here, we present a guideline for quality management systems (QMS) for academic organizations incorporating the essential components while confining the requirements to an easily manageable effort. It provides a starting point to implement a QMS tailored to specific needs effortlessly and greatly facilitates technology transfer in a controlled manner, thereby supporting reproducibility and reusability. Ultimately, the emerging standardized workflows can pave the way for an accelerated deployment in clinical practice.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; health informatics; software engineering; software robustness.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson D.J. Blue Hole Press; 2010. Kanban: Successful Evolutionary Change for Your Technology Business.
-
- Anwar S.M., Majid M., Qayyum A., Awais M., Alnowami M., Khan M.K. Medical image analysis using convolutional neural networks: a review. J. Med. Syst. 2018;42:226. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources