Reduced-intensity conditioning hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter's transformation
- PMID: 34297048
- PMCID: PMC8341347
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003726
Reduced-intensity conditioning hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter's transformation
Abstract
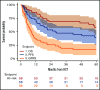
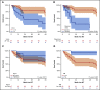
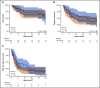
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) may potentially cure patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and Richter's transformation (CLL-RT) or CLL without RT, but the impact of novel agents on HSCT is unclear. CLL-RT patients have a grave prognosis, and their outcomes after HSCT are uncertain. We conducted a retrospective analysis of all 58 CLL patients, including 23 CLL-RT patients, who underwent reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) HSCT at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (New York, NY) between September 2006 and April 2017. With a median follow-up of 68 months (range, 24-147 months), 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 40% (95% confidence interval [CI], 28%-56%), and overall survival (OS) was 58% (95% CI, 48%-74%). The 1-year graft-versus-host disease/relapse-free survival (GRFS) was 38% (95% CI, 25%-50%). Patients with CLL-RT and CLL patients without RT had comparable outcomes. In both cohorts, treatment-sensitive response and ≤3 previous lines of therapy produced superior PFS and OS. Outcomes were agnostic to adverse cytogenetic and molecular features. Novel agents did not have a negative impact on HSCT outcomes. Total body irradiation (TBI)-containing RIC yielded inferior PFS, OS, and GRFS. CLL-RT patients older than age 55 years who had an HSCT Comorbidity Index score of ≥2 demonstrated inferior OS. This study, which is the largest series of RIC-HSCT for patients with CLL-RT, provides evidence supporting RIC-HSCT in early remission courses for patients with CLL-RT and poor-risk CLL patients. TBI-containing RIC should be considered with caution.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures


References
-
- Tsimberidou AM, Keating MJ.. Richter syndrome: biology, incidence, and therapeutic strategies. Cancer. 2005;103(2):216-228. - PubMed
-
- Bockorny B, Codreanu I, Dasanu CA.. Hodgkin lymphoma as Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a retrospective analysis of world literature. Br J Haematol. 2012;156(1):50-66. - PubMed
-
- Tsimberidou AM, O’Brien S, Khouri I, et al. Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors in patients with Richter’s syndrome treated with chemotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy with or without stem-cell transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(15):2343-2351. - PubMed
-
- Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Bazarbachi A.. Hematopoietic stem cell allografting for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a focus on reduced-intensity conditioning regimens. Cancer Contr. 2012;19(1):68-75. - PubMed
-
- Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Kumar A, Hamadani M, et al. Clinical practice recommendations for use of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia on behalf of the Guidelines Committee of the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(12):2117-2125. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

