The Effects of Malaria in Pregnancy on Neurocognitive Development in Children at 1 and 6 Years of Age in Benin: A Prospective Mother-Child Cohort
- PMID: 34297062
- PMCID: PMC8906760
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciab569
The Effects of Malaria in Pregnancy on Neurocognitive Development in Children at 1 and 6 Years of Age in Benin: A Prospective Mother-Child Cohort
Abstract
Background: Malaria in pregnancy (MiP) contributes significantly to infant mortality rates in sub-Saharan Africa and has consequences on survivors, such as preterm birth and low birth weight. However, its impact on long-term neurocognitive development in children remains unknown.
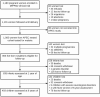
Methods: Our prospective cohort included pregnant women and their live-born singletons from the Malaria in Pregnancy Preventive Alternative Drugs clinical trial. MiP was assessed using microscopy and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Neurocognitive development in children was assessed using the Mullen Scales of Early Learning and the Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children, 2nd edition (KABC-II), at 1 and 6 years of age, respectively.
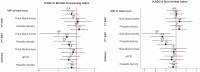
Results: Of 493 pregnant women, 196 (40%) were infected with malaria at least once: 121 (31%) with placental malaria diagnosed by qPCR. Multiple linear regression B-coefficients showed that impaired gross motor scores were associated with MiP at least once (-2.55; confidence interval [95% CI]: -5.15, 0.05), placental malaria by qPCR (-4.95; 95% CI: -7.65, -2.24), and high parasite density at delivery (-1.92; 95% CI: -3.86, 0.02) after adjustment. Malaria and high parasite density at the second antenatal care visit were associated with lower KABC-II Non-Verbal Index scores at 6 years (-2.57 [95% CI: -4.86, -0.28] and -1.91 [-3.51, -0.32]), respectively.
Conclusions: This prospective cohort study provides evidence that MiP, particularly late term, could have important negative consequences on child development at 1 and 6 years of age. Mechanisms behind this association must be further investigated and diagnostic methods in low-income countries should be strengthened to provide adequate treatment.
Clinical trials registration: NCT00811421.
Keywords: child development; malaria; neurocognition; pregnancy; sub-Saharan Africa.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- Desai M, ter Kuile FO, Nosten F, et al. . Epidemiology and burden of malaria in pregnancy. Lancet Infect Dis 2007; 7:93-104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 2015 00060746/Fondation de France
- R21 HD060524/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- EDCTP- IP.07.31080.002/European and Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership
- NIH/NICHD- R21-HD060524/Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
- Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation

