Ultrasound-guided injection of intralesional steroids in acute hidradenitis suppurativa lesions: A prospective study
- PMID: 34297465
- PMCID: PMC9285692
- DOI: 10.1111/dth.15068
Ultrasound-guided injection of intralesional steroids in acute hidradenitis suppurativa lesions: A prospective study
Abstract
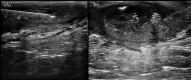
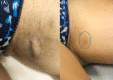
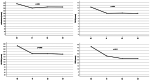
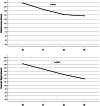
The management of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) flares with intralesional steroids lacks strong scientific evidence but limited data suggest that it may be useful. The objective of this study is to assess the clinical and ultrasound responses of HS flares to ultrasound-guided injections of intralesional triamcinolone (40 mg/ml) with a dilution 1:4 versus 1:2 at 30-day (t1), 60-day (t2), and 90-day (t3) follow-up. We recruited patients with ≤3 acute lesions, unresponsive to topical therapy. At baseline we assessed lesions clinically and by ultra-high frequency ultrasound (48 or 70 MHz) and randomly performed an ultrasound-guided injection of triamcinolone. Assessments were repeated at t1, t2, and t3 follow-up, re-injecting the lesion in the case of no or partial response. We treated 49 lesions: 38.8% showed improvements at t1; 46.9% at t2; 6% at t3; and 8.3% showed no clinical and ultrasound improvements. Long-term follow-up data confirmed a statistically significant reduction in Visual Analogue Scale (VAS)-pain, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), and HS-Physician Global Assessment (HS-PGA), as well as edema and vascular signals. No adverse effects were reported. Our study suggests that ultrasound-injections with a 1:2 dilution are beneficial for HS flares that do not respond to topical treatment and should be included in the therapeutic algorithm.
Keywords: HS flares; acute flare management; hidradenitis suppurativa; intralesional steroids; ultrasound guided injections.
© 2021 The Authors. Dermatologic Therapy published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures


Comment in
-
Intralesional steroid injections to target sinus tract fibrosis in hidradenitis suppurativa: Results from an ultrasound-based retrospective study.Dermatol Ther. 2022 Sep;35(9):e15710. doi: 10.1111/dth.15710. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Dermatol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35811390 No abstract available.
-
Management of scarring HS fistulas with intralesional steroids.Dermatol Ther. 2022 Sep;35(9):e15708. doi: 10.1111/dth.15708. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Dermatol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35811401 No abstract available.
References
-
- Zouboulis CC, Desai N, Emtestam L, et al. European S1 guideline for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:619‐644. - PubMed
-
- Wortsman X, Moreno C, Soto R, Arellano J, Pezo C, Wortsman J. Ultrasound in‐depth characterization and staging of hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:1835‐1842. - PubMed
-
- Napolitano M, Calzavara‐Pinton PG, Zanca A, et al. Comparison of clinical and ultrasound scores in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: results from an Italian ultrasound working group. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:e84‐e87. - PubMed
-
- Lacarrubba F, Dini V, Napolitano M, et al. Ultrasonography in the pathway to an optimal standard of care of hidradenitis suppurativa: the Italian ultrasound working group experience. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33(Suppl 6):10‐14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

