Systems-Level Change to Alleviate Barriers to Cancer Clinical Trial Access for Adolescents and Young Adults in Australia
- PMID: 34297611
- PMCID: PMC9057899
- DOI: 10.1089/jayao.2021.0026
Systems-Level Change to Alleviate Barriers to Cancer Clinical Trial Access for Adolescents and Young Adults in Australia
Abstract
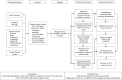
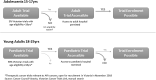
Purpose: International data demonstrate association between clinical trial participation and reduced cancer mortality. Adolescents and young adults (AYA) have low clinical trial enrollment rates. We established a program to understand local barriers and develop targeted solutions that lead to greater AYA clinical trial participation. Methods: A steering committee (SC) with expertise in adult and pediatric oncology, research ethics, and consumer representation was formed. The SC mapped barriers related to AYA trial access and established working groups (WGs) around three themes. Results: The Regulatory Awareness WG identified a lack of understanding of processes that support protocol approval for clinical trials across the AYA age range. A guideline to raise awareness was developed. The Access WG identified challenges for young adults (18-25 years) to access a pediatric hospital to enroll in a pediatric trial. A procedure was developed to streamline applications for access. The first six applications using this procedure have been successful. The Availability WG identified lack of pediatric-adult oncology reciprocal relationships as a barrier to awareness of open trials, and future collaboration. An AYA Craft Group Framework was established to grow relationships within tumor streams across institutions; two craft groups are now operating locally. An additional achievement was a successful request to the Therapeutic Goods Administration for Australian adoption of the Food and Drug Administration Guidance on Considerations for the Inclusion of Adolescent Patients in Adult Oncology Clinical Trials. Conclusion: This multipronged approach to improving AYA clinical trial access has relevance for other health environments. Our knowledge products are available as an online toolkit.
Keywords: access; barriers; clinical trials; system.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
