Recruitment of a multi-site randomized controlled trial of aerobic exercise for older adults with amnestic mild cognitive impairment: The EXERT trial
- PMID: 34297895
- PMCID: PMC9292825
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.12401
Recruitment of a multi-site randomized controlled trial of aerobic exercise for older adults with amnestic mild cognitive impairment: The EXERT trial
Abstract
Introduction: Effective strategies to recruit older adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) into nonpharmacological intervention trials are lacking.
Methods: Recruitment for EXERT, a multisite randomized controlled 18-month trial examining the effects of aerobic exercise on cognitive trajectory in adults with amnestic MCI, involved a diverse portfolio of strategies to enroll 296 participants.
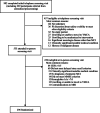
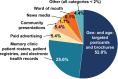
Results: Recruitment occurred September 2016 through March 2020 and was initially slow. After mass mailings of 490,323 age- and geo-targeted infographic postcards and brochures, recruitment rates increased substantially, peaking at 16 randomizations/month in early 2020. Mass mailings accounted for 52% of randomized participants, whereas 25% were recruited from memory clinic rosters, electronic health records, and national and local registries. Other sources included news broadcasts, public service announcements (PSA), local advertising, and community presentations.
Discussion: Age- and geo-targeted mass mailing of infographic materials was the most effective approach in recruiting older adults with amnestic MCI into an 18-month exercise trial.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; clinical trial; exercise; lifestyle intervention; mild cognitive impairment; nonpharmacological; recruitment.
© 2021 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
AHS, AZL, OCO, SPT, JKF, GM, DB, AAS, KAS, RHM, SAK, JM, DT, RGT, CWC, and LDB have no conflicts of interest. HHF reports UCSD service agreements for consulting with Axon Neuroscience, Banner Health, Roche/Genentech (DMC and DSMB), Samus Therapeutics, Tau Consortium, Novo Nordisk, and Janssen; ADCS Clinical Trials grant funding from Annovis (Posiphen), Biohaven (BH 4157), Vivoryon (PQ 912), AC Immune (ACI‐24‐1301), LuMind (ADC‐059‐LIFE‐DSR); and Research funding from NIA/NIH (U19 AG010483, P30 AG062429, R01 AG061146‐01, 1R56AG069130‐01, R01 AG051618), CIHR (137794, 254450, 294127), Brain Canada (4469), and Alzheimer's Association (SG‐20‐690388‐PEACE AD). KWB reports grants from VeraSci Inc. and personal fees from Biogen. CVD reports consulting fees from Roche and Eisai and grants for clinical trials from Biogen, Roche, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Genentech, Janssen, Novartis, Biohaven, and Merck.
Figures

References
-
- Sanders ML, Stuckenschneider T, Devenney KE, et al. Real world recruiting of older subjects with mild cognitive impairment for exercise trials: community readiness is pivotal. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;62(2):579‐581. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

