A reexamination of motor and prefrontal TMS in tobacco use disorder: Time for personalized dosing based on electric field modeling?
- PMID: 34298414
- PMCID: PMC8384673
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinph.2021.06.015
A reexamination of motor and prefrontal TMS in tobacco use disorder: Time for personalized dosing based on electric field modeling?
Abstract
Objective: In this study, we reexamined the use of 120% resting motor threshold (rMT) dosing for transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) over the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) using electric field modeling.
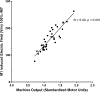
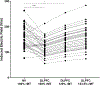
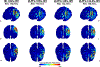
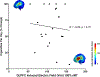
Methods: We computed electric field models in 38 tobacco use disorder (TUD) participants to compare figure-8 coil induced electric fields at 100% rMT over the primary motor cortex (M1), and 100% and 120% rMT over the DLPFC. We then calculated the percentage of rMT needed for motor-equivalent induced electric fields at the DLPFC and modeled this intensity for each person.
Results: Electric fields from 100% rMT stimulation over M1 were significantly larger than what was modeled in the DLPFC using 100% rMT (p < 0.001) and 120% rMT stimulation (p = 0.013). On average, TMS would need to be delivered at 133.5% rMT (range = 79.9 to 247.5%) to produce motor-equivalent induced electric fields at the DLPFC of 158.2 V/m.
Conclusions: TMS would have to be applied at an average of 133.5% rMT over the left DLPFC to produce equivalent electric fields to 100% rMT stimulation over M1 in these 38 TUD patients. The high interindividual variability between motor and prefrontal electric fields for each participant supports using personalized electric field modeling for TMS dosing to ensure that each participant is not under- or over-stimulated.
Significance: These electric field modeling in TUD data suggest that 120% rMT stimulation over the DLPFC delivers sub-motor equivalent electric fields in many individuals (73.7%). With further validation, electric field modeling may be an impactful method of individually dosing TMS.
Keywords: Electric field modeling; Finite element method; Motor threshold; Personalized dosing; Tobacco use disorder; Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS).
Copyright © 2021 International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Blumberger DM, Vila-Rodriguez F, Thorpe KE, Feffer K, Noda Y, Giacobbe P, et al. (2018). Effectiveness of theta burst versus high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in patients with depression (THREE-D): a randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet, 391(10131), 1683–1692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

