Ultrasound-Mediated Cavitation Enhances EGFR-Targeting PLGA-PEG Nano-Micelle Delivery for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 34298600
- PMCID: PMC8304156
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13143383
Ultrasound-Mediated Cavitation Enhances EGFR-Targeting PLGA-PEG Nano-Micelle Delivery for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Treatment
Abstract
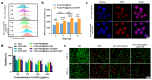
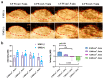
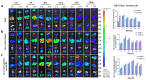
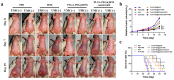
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is highly recurring and metastatic breast cancer with overexpressing epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Herein, a series of in vitro and in vivo analyses were used to explore the therapeutic effect of EGFR-targeting nano-micelles (PLGA-PEG/DOX@anti-EGFR) combined with ultrasound-mediated cavitation (UMC). The prepared nano-micelle drug carriers have good biocompatibility and can greatly increase the drug accumulation in tumor regions, thereby reducing off-target toxicity while enhancing anti-tumor efficacy. Moreover, an in vivo analysis of the practical utility of this treatment modality was conducted by using SonoVueTM microbubbles to achieve cavitation under different power intensity levels, with an ultrasonic power intensity of 0.5 W/cm2 maximizing the intra-tumoral blood perfusion. Relative to PLGA-PEG@DOX/anti-EGFR nano-micelles treatment alone, the combination with UMC was better able to suppress tumor growth even at low concentrations. As such, combining actively targeted drug-carrier molecules with UMC represents an effective approach to enhancing therapeutic efficacy while reducing the adverse, systemic effects associated with DOX and other chemotherapeutic drugs, and it can be considered as a promising clinical prospect in the treatment of TNBC.
Keywords: DOX; EGFR-targeting; PLGA nano-micelle; SonoVueTM; triple-negative breast cancer; ultrasound-mediated cavitation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

