Hypoxia in Lung Cancer Management: A Translational Approach
- PMID: 34298636
- PMCID: PMC8307602
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13143421
Hypoxia in Lung Cancer Management: A Translational Approach
Abstract
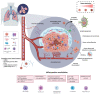
Lung cancer represents the first cause of death by cancer worldwide and remains a challenging public health issue. Hypoxia, as a relevant biomarker, has raised high expectations for clinical practice. Here, we review clinical and pathological features related to hypoxic lung tumours. Secondly, we expound on the main current techniques to evaluate hypoxic status in NSCLC focusing on positive emission tomography. We present existing alternative experimental approaches such as the examination of circulating markers and highlight the interest in non-invasive markers. Finally, we evaluate the relevance of investigating hypoxia in lung cancer management as a companion biomarker at various lung cancer stages. Hypoxia could support the identification of patients with higher risks of NSCLC. Moreover, the presence of hypoxia in treated tumours could help clinicians predict a worse prognosis for patients with resected NSCLC and may help identify patients who would benefit potentially from adjuvant therapies. Globally, the large quantity of translational data incites experimental and clinical studies to implement the characterisation of hypoxia in clinical NSCLC management.
Keywords: HIF; angiogenesis; hypoxia; lung cancer management; non-small cell lung cancer; oxygen sensing.
Conflict of interest statement
G.D. reports personal fees from Nuvaira, personal fees from BTG/PneumRx, personal fees from Chiesi, personal fees from Boehringer, personal fees from Astra Zeneca, outside the submitted work. V.D. (Valérian Dormoy). reports personal fees from Chiesi outside the submitted work. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

