Applications of Radiolabelled Curcumin and Its Derivatives in Medicinal Chemistry
- PMID: 34299029
- PMCID: PMC8306375
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22147410
Applications of Radiolabelled Curcumin and Its Derivatives in Medicinal Chemistry
Abstract
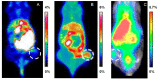
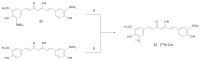
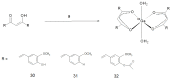
Curcumin is a natural occurring molecule that has aroused much interest among researchers over the years due to its pleiotropic set of biological properties. In the nuclear medicine field, radiolabelled curcumin and curcumin derivatives have been studied as potential radiotracers for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and cancer. In the present review, the synthetic pathways, labelling methods and the preclinical investigations involving these radioactive compounds are treated. The studies entailed chemical modifications for enhancing curcumin stability, as well as its functionalisation for the labelling with several radiohalogens or metal radionuclides (fluorine-18, technetium-99m, gallium-68, etc.). Although some drawbacks have yet to be addressed, and none of the radiolabelled curcuminoids have so far achieved clinical application, the studies performed hitherto provide useful insights and lay the foundation for further developments.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; curcumin; curcuminoids; radioactive labelling; radionuclides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
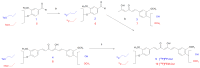
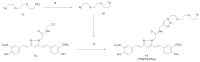

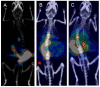

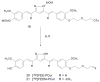
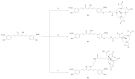

References
-
- Lampe V. Synthese von Curcumin. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1918;51:1347–1355. doi: 10.1002/cber.19180510223. - DOI
-
- Zerazion E., Rosa R., Ferrari E., Veronesi P., Leonelli C., Saladini M., Ferrari A.M. Phytochemical compounds or their synthetic counterparts? A detailed comparison of the quantitative environmental assessment for the synthesis and extraction of curcumin. Green Chem. 2016;18:1807–1818. doi: 10.1039/C6GC00090H. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

