Antiproliferative Properties and G-Quadruplex-Binding of Symmetrical Naphtho[1,2-b:8,7-b']dithiophene Derivatives
- PMID: 34299583
- PMCID: PMC8303715
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26144309
Antiproliferative Properties and G-Quadruplex-Binding of Symmetrical Naphtho[1,2-b:8,7-b']dithiophene Derivatives
Abstract
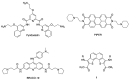
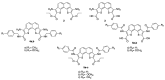
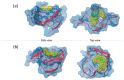
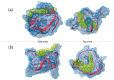
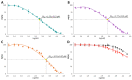
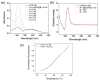
Background: G-quadruplex (G4) forming sequences are recurrent in telomeres and promoter regions of several protooncogenes. In normal cells, the transient arrangements of DNA in G-tetrads may regulate replication, transcription, and translation processes. Tumors are characterized by uncontrolled cell growth and tissue invasiveness and some of them are possibly mediated by gene expression involving G-quadruplexes. The stabilization of G-quadruplex sequences with small molecules is considered a promising strategy in anticancer targeted therapy. Methods: Molecular virtual screening allowed us identifying novel symmetric bifunctionalized naphtho[1,2-b:8,7-b']dithiophene ligands as interesting candidates targeting h-Telo and c-MYC G-quadruplexes. A set of unexplored naphtho-dithiophene derivatives has been synthesized and biologically tested through in vitro antiproliferative assays and spectroscopic experiments in solution. Results: The analysis of biological and spectroscopic data highlighted noteworthy cytotoxic effects on HeLa cancer cell line (GI50 in the low μM range), but weak interactions with G-quadruplex c-MYC promoter. Conclusions: The new series of naphtho[1,2-b:8,7-b']dithiophene derivatives, bearing the pharmacophoric assumptions necessary to stabilize G-quadruplexes, have been designed and successfully synthesized. The interesting antiproliferative results supported by computer aided rational approaches suggest that these studies are a significant starting point for a lead optimization process and the isolation of a more efficacious set of G-quadruplexes stabilizers.
Keywords: G-Quadruplex; antiproliferative effect; c-MYC; h-Telo; molecular docking; planar heterocyclic scaffold; synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Neidle S. Quadruplex nucleic acids as targets for anticancer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017;1:41. doi: 10.1038/s41570-017-0041. - DOI
-
- Lauria A., Terenzi A., Bartolotta R., Bonsignore R., Perricone U., Tutone M., Martorana A., Barone G., Almerico A.M. Does ligand symmetry play a role in the stabilization of DNA G-quadruplex host-guest complexes? Curr. Med. Chem. 2014;21:2665–2690. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666140217155156. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 161161/PJ_RIC_FFABR_2017_161161 Grant-University of Palermo
- ARS01_00432/European Union 2014-2020 PON Ricerca e Innovazione grant from the Italian Ministry of Edu-cation, University and Research, entitled "PROGEMA-Processi Green per l'Estrazione di Prin-cipi Attivi e la Depurazione di Matrici di Scarto e Non"

