Novel Approach Sizing and Routing of Wireless Sensor Networks for Applications in Smart Cities
- PMID: 34300432
- PMCID: PMC8309638
- DOI: 10.3390/s21144692
Novel Approach Sizing and Routing of Wireless Sensor Networks for Applications in Smart Cities
Abstract
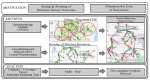
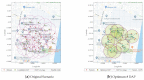
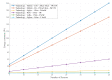
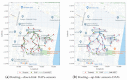
Citizens are expected to require the growth of multiple Internet of Things (IoT) -based applications to improve public and private services. According to their concept, smart cities seek to improve the efficiency, reliability, and resilience of these services. Consequently, this paper searches for a new vision for resolving problems related to the quick deployment of a wireless sensor network (WSN) by using a sizing model and considering the capacity and coverage of the concentrators. Additionally, three different routing models of these technology resources are presented as alternatives for each WSN deployment to ensure connectivity between smart meters and hubs required for smart metering. On the other hand, these solutions must reduce costs when this type of wireless communication network is deployed. The present work proposes various optimization models that consider the physical and network layers in order to integrate different wireless communication technologies, thus reducing costs in terms of the minimum number of data aggregation points. Using a heterogeneous wireless network can reduce resource costs and energy consumption in comparison to a single cellular technology, as proposed in previous works. This work proposes a sizing model and three different models for routing wireless networks. In each case, constraints are evaluated and can be associated with different real-world scenarios. This document provides an optimization model that encompasses all of the proposed constraints; due to the combinatorial nature of the problem, this would require a heuristic technique.
Keywords: MST; internet of things; optimization; routing; sizing; smart cities; smart metering; wireless sensor networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Khalil M., Khalid A., Khan F.U., Shabbir A. A review of routing protocol selection for wireless sensor networks in smart cities; Proceedings of the 24th Asia-Pacific Conference on Communications, APCC; Ningbo, China. 12–14 November 2018; pp. 610–615. - DOI
-
- Afaneh A., Shahrour I. Use of GIS for SunRise Smart City project, large scale demonstrator of the Smart City. SENSET. 2017;2017:1–4. doi: 10.1109/SENSET.2017.8125071. - DOI
-
- Jain B., Brar G., Malhotra J., Rani S. A novel approach for smart cities in convergence to wireless sensor networks. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017;35:440–448. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2017.08.005. - DOI
-
- S S.N., Mane P.B. Swarm Intelligent WSN for Smart City. Proc. Int. Conf. Data Eng. Commun. Technol. 2017;469:603–611. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-1678-3. - DOI
-
- Jawhar I., Mohamed N., Al-Jaroodi J. Networking architectures and protocols for smart city systems. J. Internet Serv. Appl. 2018;9 doi: 10.1186/s13174-018-0097-0. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

