Novel Chemical Architectures Based on Beta-Cyclodextrin Derivatives Covalently Attached on Polymer Spheres
- PMID: 34301095
- PMCID: PMC8309509
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13142338
Novel Chemical Architectures Based on Beta-Cyclodextrin Derivatives Covalently Attached on Polymer Spheres
Abstract
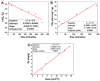
This study presents the synthesis and characterization of polymer derivatives of beta-cyclodextrin (BCD), obtained by chemical grafting onto spherical polymer particles (200 nm) presenting oxirane functional groups at their surface. The polymer spheres were synthesized by emulsion polymerization of styrene (ST) and hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA), followed by the grafting on the surface of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) by seeded emulsion polymerization. The BCD-polymer derivatives were obtained using two BCD derivatives with hydroxylic (BCD-OH) and amino groups (BCD-NH2). The degree of polymer covalent functionalization using the BCD-OH and BCD-NH2 derivatives were determined to be 4.27 and 19.19 weight %, respectively. The adsorption properties of the materials were evaluated using bisphenol A as a target molecule. The best fit for the adsorption kinetics was Lagergren's model (both for Qe value and for R2) together with Weber's intraparticle diffusion model in the case of ST-HEMA-GMA-BCD-NH2. The isothermal adsorption evaluation indicated that both systems follow a Langmuir type behavior and afforded a Qmax value of 148.37 mg g-1 and 37.09 mg g-1 for ST-HEMA-GMA-BCD-NH2 and ST-HEMA-GMA-BCD-OH, respectively. The BCD-modified polymers display a degradation temperature of over 400 °C which can be attributed to the existence of hydrogen bonds and BCD thermal degradation pathway in the presence of the polymers.
Keywords: adsorption isotherms; adsorption kinetics; beta-cyclodextrin; bisphenol A adsorption; emulsion polymerization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Bisphenol A Adsorption on Silica Particles Modified with Beta-Cyclodextrins.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Dec 23;12(1):39. doi: 10.3390/nano12010039. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35009992 Free PMC article.
-
Functionalized cellulose with hydroxyethyl methacrylate and glycidyl methacrylate for metal ions and dye adsorption applications.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Aug 1;134:704-721. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.059. Epub 2019 May 10. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 31082422
-
Superparamagnetic polymer emulsion particles from a soap-free seeded emulsion polymerization and their application for lipase immobilization.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014 Jan;172(2):701-12. doi: 10.1007/s12010-013-0563-x. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24114322
-
Recent environmental applications of and development prospects for immobilized laccase: a review.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2020 Oct;36(2):81-131. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2020.1864187. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2020. PMID: 33435852 Review.
-
Adsorption of plasma proteins onto polymer latices.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 1991 Mar;35:139-72. doi: 10.1016/0001-8686(91)80021-b. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 1991. PMID: 2043288 Review.
Cited by
-
Bisphenol A Adsorption on Silica Particles Modified with Beta-Cyclodextrins.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Dec 23;12(1):39. doi: 10.3390/nano12010039. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35009992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ohore O.E., Zhang S. Endocrine disrupting effects of bisphenol A exposure and recent advances on its removal by water treatment systems. A review. Sci. Afr. 2019;5:e00135. doi: 10.1016/j.sciaf.2019.e00135. - DOI
-
- Bolong N., Ismail A.F., Salim M.R., Rana D., Matsuura T., Tabe-Mohammadi A. Negatively charged polyethersulfone hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane for the removal of bisphenol A from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010;73:92–99. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2010.01.001. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

