Understanding the complexities of antibiotic prescribing behaviour in acute hospitals: a systematic review and meta-ethnography
- PMID: 34301332
- PMCID: PMC8299683
- DOI: 10.1186/s13690-021-00624-1
Understanding the complexities of antibiotic prescribing behaviour in acute hospitals: a systematic review and meta-ethnography
Abstract
Background: Antimicrobial resistance poses a serious global public health threat. Hospital misuse of antibiotics has contributed to this problem and evidence-based interventions are urgently needed to change inappropriate prescribing practices. This paper reports the first theoretical stage of a longer-term project to improve antibiotic prescribing in hospitals through design of an effective behaviour-change intervention.
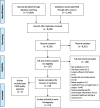
Methods: Qualitative synthesis using meta-ethnography of primary studies reporting doctors' views and experiences of antibiotic prescribing in hospitals for example, their barriers to appropriate prescribing. Twenty electronic databases were systematically searched over a 10-year period and potential studies screened against eligibility criteria. Included studies were quality-appraised. Original participant quotes and author interpretations were extracted and coded thematically into NVivo. All study processes were conducted by two reviewers working independently with findings discussed with the wider team and key stakeholders. Studies were related by findings into clusters and translated reciprocally and refutationally to develop a new line-of-argument synthesis and conceptual model. Findings are reported using eMERGe guidance.
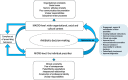
Results: Fifteen papers (13 studies) conducted between 2007 and 2017 reporting the experiences of 336 doctors of varying seniority working in acute hospitals across seven countries, were synthesised. Study findings related in four ways which collectively represented multiple challenges to appropriate antibiotic medical prescribing in hospitals: loss of ownership of prescribing decisions, tension between individual care and public health concerns, evidence-based practice versus bedside medicine, and diverse priorities between different clinical teams. The resulting new line-of-argument and conceptual model reflected how these challenges operated on both micro- and macro-level, highlighting key areas for improving current prescribing practice, such as creating feedback mechanisms, normalising input from other specialties and reducing variation in responsibility for antibiotic decisions.
Conclusions: This first meta-ethnography of doctors` experiences of antibiotic prescribing in acute hospital settings has enabled development of a novel conceptual model enhancing understanding of appropriate antibiotic prescribing. That is, hospital antibiotic prescribing is a complex, context-dependent and dynamic process, entailing the balancing of many tensions. To change practice, comprehensive efforts are needed to manage failures in communication and information provision, promote distribution of responsibility for antibiotic decisions, and reduce fear of consequences from not prescribing.
Trial registration: PROSPERO registration: CRD42017073740 .
Keywords: Acute hospitals; Antibiotic decision-making; Antimicrobial resistance; Doctors; Meta-ethnography; Prescribing behaviour; Qualitative synthesis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Barber S, Swaden-Lewis K Briefing Paper, Antimicrobial Resistance - House of Commons Library. Briefing Paper. 2017. https://commonslibrary.parliament.uk/research-briefings/cbp-8141/. Accessed 19 Aug 2019.
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in Europe Annual report of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net) 2018. 2019. 10.2900/230516.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources