Temperature dependence of spontaneous mutation rates
- PMID: 34301628
- PMCID: PMC8415371
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.275168.120
Temperature dependence of spontaneous mutation rates
Abstract
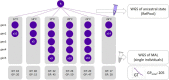
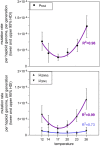
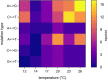
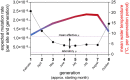
Mutation is the source of genetic variation and the fundament of evolution. Temperature has long been suggested to have a direct impact on realized spontaneous mutation rates. If mutation rates vary in response to environmental conditions, such as the variation of the ambient temperature through space and time, they should no longer be described as species-specific constants. By combining mutation accumulation with whole-genome sequencing in a multicellular organism, we provide empirical support to reject the null hypothesis of a constant, temperature-independent mutation rate. Instead, mutation rates depended on temperature in a U-shaped manner with increasing rates toward both temperature extremes. This relation has important implications for mutation-dependent processes in molecular evolution, processes shaping the evolution of mutation rates, and even the evolution of biodiversity as such.
© 2021 Waldvogel and Pfenninger; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic modifications affect the rate of spontaneous mutations in a pathogenic fungus.Nat Commun. 2021 Oct 7;12(1):5869. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26108-y. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34620872 Free PMC article.
-
Old Trade, New Tricks: Insights into the Spontaneous Mutation Process from the Partnering of Classical Mutation Accumulation Experiments with High-Throughput Genomic Approaches.Genome Biol Evol. 2019 Jan 1;11(1):136-165. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evy252. Genome Biol Evol. 2019. PMID: 30476040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yeast Spontaneous Mutation Rate and Spectrum Vary with Environment.Curr Biol. 2019 May 20;29(10):1584-1591.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.03.054. Epub 2019 May 2. Curr Biol. 2019. PMID: 31056389 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Mutation Rate Response to pH Change in the Coral Reef Pathogen Vibrio shilonii AK1.mBio. 2017 Aug 22;8(4):e01021-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01021-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28830944 Free PMC article.
-
Causes of Mutation Rate Variability in Plant Genomes.Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2023 May 22;74:751-775. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-070522-054109. Epub 2023 Mar 8. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 36889008 Review.
Cited by
-
Human DNA Mutations and their Impact on Genetic Disorders.Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2024;18(4):288-315. doi: 10.2174/0118722083255081231020055309. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37936448 Review.
-
Genomic estimates of mutation and substitution rates contradict the evolutionary speed hypothesis of the latitudinal diversity gradient.Proc Biol Sci. 2023 Oct 25;290(2009):20231787. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2023.1787. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Proc Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37876195 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in mutation, recombination, and transposition rates in Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila simulans.Genome Res. 2023 Apr;33(4):587-598. doi: 10.1101/gr.277383.122. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Genome Res. 2023. PMID: 37037625 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of genetic diversity in Neotropical salamanders (Plethodontidae: Bolitoglossini).Ecol Evol. 2023 Nov 16;13(11):e10707. doi: 10.1002/ece3.10707. eCollection 2023 Nov. Ecol Evol. 2023. PMID: 38020701 Free PMC article.
-
Abiotic selection of microbial genome size in the global ocean.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 13;14(1):1384. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36988-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36914646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal AF. 2002. Genetic loads under fitness-dependent mutation rates. J Evol Biol 15: 1004–1010. 10.1046/j.1420-9101.2002.00464.x - DOI
-
- Bååth R. 2014. Bayesian first aid: a package that implements Bayesian alternatives to the classical *.test functions in R. Proc UseR 33: 2.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
