Missing Self-Induced Microvascular Rejection of Kidney Allografts: A Population-Based Study
- PMID: 34301794
- PMCID: PMC8455279
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2020111558
Missing Self-Induced Microvascular Rejection of Kidney Allografts: A Population-Based Study
Abstract
Background: Circulating anti-HLA donor-specific antibodies (HLA-DSA) are often absent in kidney transplant recipients with microvascular inflammation (MVI). Missing self, the inability of donor endothelial cells to provide HLA I-mediated signals to inhibitory killer cell Ig-like receptors (KIRs) on recipient natural killer cells, can cause endothelial damage in vitro, and has been associated with HLA-DSA-negative MVI. However, missing self's clinical importance as a nonhumoral trigger of allograft rejection remains unclear.
Methods: In a population-based study of 924 consecutive kidney transplantations between March 2004 and February 2013, we performed high-resolution donor and recipient HLA typing and recipient KIR genotyping. Missing self was defined as the absence of A3/A11, Bw4, C1, or C2 donor genotype, with the presence of the corresponding educated recipient inhibitory KIR gene.
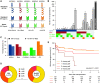
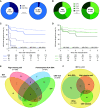
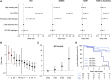
Results: We identified missing self in 399 of 924 transplantations. Co-occurrence of missing self types had an additive effect in increasing MVI risk, with a threshold at two concurrent types (hazard ratio [HR], 1.78; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 1.26 to 2.53), independent of HLA-DSA (HR, 5.65; 95% CI, 4.01 to 7.96). Missing self and lesions of cellular rejection were not associated. No HLA-DSAs were detectable in 146 of 222 recipients with MVI; 28 of the 146 had at least two missing self types. Missing self associated with transplant glomerulopathy after MVI (HR, 2.51; 95% CI, 1.12 to 5.62), although allograft survival was better than with HLA-DSA-associated MVI.
Conclusion: Missing self specifically and cumulatively increases MVI risk after kidney transplantation, independent of HLA-DSA. Systematic evaluation of missing self improves understanding of HLA-DSA-negative MVI and might be relevant for improved diagnostic classification and patient risk stratification.
Keywords: antibody-mediated rejection; kidney transplantation; microvascular inflammation; missing self; natural killer cells.
Copyright © 2021 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Samaniego M, Becker BN, Djamali A: Drug insight: maintenance immunosuppression in kidney transplant recipients. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 2: 688–699, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Halloran PF: Immunosuppressive drugs for kidney transplantation. N Engl J Med 351: 2715–2729, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Coemans M, Süsal C, Döhler B, Anglicheau D, Giral M, Bestard O, et al. .: Analyses of the short- and long-term graft survival after kidney transplantation in Europe between 1986 and 2015. Kidney Int 94: 964–973, 2018 - PubMed
-
- Lamb KE, Lodhi S, Meier-Kriesche HU: Long-term renal allograft survival in the United States: A critical reappraisal. Am J Transplant 11: 450–462, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Meier-Kriesche HU, Schold JD, Srinivas TR, Kaplan B: Lack of improvement in renal allograft survival despite a marked decrease in acute rejection rates over the most recent era. Am J Transplant 4: 378–383, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

