First-line avelumab in a cohort of 116 patients with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma (JAVELIN Merkel 200): primary and biomarker analyses of a phase II study
- PMID: 34301810
- PMCID: PMC8311489
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002646
First-line avelumab in a cohort of 116 patients with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma (JAVELIN Merkel 200): primary and biomarker analyses of a phase II study
Abstract
Background: Avelumab (anti-programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1)) is approved in multiple countries for the treatment of metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma (mMCC), a rare and aggressive skin cancer. We report efficacy and safety data and exploratory biomarker analyses from a cohort of patients with mMCC treated with first-line avelumab in a phase II trial.
Methods: Patients with treatment-naive mMCC received avelumab 10 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks. The primary endpoint was durable response, defined as objective response (complete or partial response; assessed by independent review) lasting ≥6 months. Additional assessments included progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), safety, and biomarker analyses.
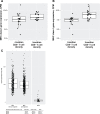
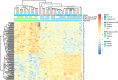
Results: In 116 patients treated with avelumab, median follow-up was 21.2 months (range: 14.9-36.6). Thirty-five patients had a response lasting ≥6 months, giving a durable response rate of 30.2% (95% CI: 22.0% to 39.4%). The objective response rate was 39.7% (95% CI: 30.7% to 49.2%). Median PFS was 4.1 months (95% CI: 1.4 to 6.1) and median OS was 20.3 months (95% CI: 12.4 to not estimable). Response rates were numerically higher in patients with PD-L1+ tumors, Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV)-negative tumors, and tumors with increased intratumoral CD8+ T-cell density. Exploratory analyses did not identify a biomarker that could reliably predict a response to first-line treatment with avelumab; however, a novel gene expression signature to identify the presence of MCPyV+ tumors was derived. Treatment-related adverse events (any grade) occurred in 94 (81.0%) patients, including grade 3/4 events in 21 (18.1%) patients; no treatment-related deaths occurred.
Conclusion: In patients with mMCC, first-line treatment with avelumab led to responses in 40% and durable responses in 30%, and was associated with a low rate of grade 3/4 treatment-related adverse events.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02155647.
Keywords: clinical trials; gene expression profiling; immunotherapy; phase II as topic; skin neoplasms; tumor biomarkers.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Dr D’Angelo reports serving as a consultant or advisor for Amgen, EMD Serono (an affiliate of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany), GlaxoSmithKline, Immune Design, Incyte, Merck & Co., and Nektar; received research grants from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Deciphera, EMD Serono, Incyte, Merck & Co., and Nektar; and received reimbursement for travel and accommodation expenses from Adaptimmune, EMD Serono, and Nektar. Dr Lebbé has received honoraria from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte, Merck & Co., Novartis, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, and Roche; reports serving as a consultant or advisor for Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck & Co., Novartis, and Roche; is a member of a speakers bureau for Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, and Roche; has received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb and Roche; has received reimbursement for travel and accommodation expenses from Bristol Myers Squibb; and has other relationships with Avantis Medical Systems. Dr Mortier has received reimbursement for travel and accommodation expenses from Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, and Roche/Genentech. Dr Brohl reports serving as a consultant or advisor for Bayer, Deciphera, EMD Serono, and PierianDx. Dr Fazio has received honoraria from Ipsen and Novartis; reports serving as a consultant or advisor for Advanced Accelerator Applications, Ipsen, Merck KGaA, MSD Oncology, Novartis/Ipsen, and Pfizer; and has received research funding from Merck KGaA and Novartis. Dr Grob has received honoraria from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck KGaA, Merck & Co., Novartis, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Roche, and Sanofi; reports serving as a consultant or advisor for Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck KGaA, Merck & Co., Novartis, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Roche, and Sanofi; is a member of a speakers’ bureau for Novartis; and has received reimbursement for travel and accommodation expenses from Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck & Co., Novartis, and Pierre Fabre. Dr Prinzi has received reimbursement for travel and accommodation expenses from Novartis. Dr Hanna has received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Exicure, GlaxoSmithKline, Kite Pharma, NantKwest/Altor BioScience, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi Genzyme, and Kartos Therapeutics; and reports receiving honoraria and serving as a consultant for Bio-Rad Laboratories, Bristol Myers Squibb, Kura Oncology, Maverick Therapeutics, Merck KGaA, Prelude Therapeutics, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals/Sanofi. Dr Hassel has received honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck & Co., Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche; reports serving as a consultant or advisor for Merck & Co. and Pierre Fabre; has received research funding from 4SC, Amgen, BioNTech, Bristol Myers Squibb, Immunocore, Novartis, Philogen, and Roche; and has received reimbursement for travel and accommodation expenses from Pierre Fabre. Dr Kiecker has received honoraria from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck & Co., Novartis, Pierre Fabre, and Roche; reports serving as a consultant or advisor for Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte, Merck & Co., Novartis, and Roche; has received research funding from Novartis; and has received reimbursement for travel and accommodation expenses from Bristol Myers Squibb and Novartis. Dr Georges reports employment at EMD Serono Research & Development Institute, Inc., an affiliate of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany. Ms Ellers-Lenz reports employment at Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany. Dr Shah reports employment at EMD Serono Research & Development Institute, Inc., an affiliate of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany. Dr Güzel reports employment at Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany. Dr Nghiem has received honoraria from EMD Serono and Merck & Co.; reports serving as a consultant or advisor for EMD Serono and Pfizer; has received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb and EMD Serono; and has a pending patent for high-affinity T-cell receptors that target the Merkel cell polyomavirus.
Figures

References
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology . Merkel cell carcinoma. V1.2020. Accessed October 17, 2020. Available: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/mcc.pdf
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
