The therapeutic and prognostic implications of immunobiology in colorectal cancer: a review
- PMID: 34302062
- PMCID: PMC8575924
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-021-01475-x
The therapeutic and prognostic implications of immunobiology in colorectal cancer: a review
Abstract
Colorectal cancer represents the second leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. The therapeutic field of immuno-oncology has rapidly gained momentum, with strikingly promising results observed in clinical practice. Increasing emphasis has been placed on the role of the immune response in tumorigenesis, therapy and predicting prognosis. Enhanced understanding of the dynamic and complex tumour-immune microenvironment has enabled the development of molecularly directed, individualised treatment. Analysis of intra-tumoural lymphocyte infiltration and the dichotomisation of colorectal cancer into microsatellite stable and unstable disease has important therapeutic and prognostic implications, with potential to capitalise further on this data. This review discusses the latest evidence surrounding the tumour biology and immune landscape of colorectal cancer, novel immunotherapies and the interaction of the immune system with each apex of the tripartite of cancer management (oncotherapeutics, radiotherapy and surgery). By utilising the synergy of chemotherapeutic agents and immunotherapies, and identifying prognostic and predictive immunological biomarkers, we may enter an era of unprecedented disease control, survivorship and cure rates.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
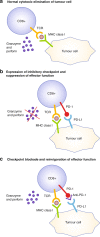
References
-
- Sauer R, Liersch T, Merkel S, Fietkau R, Hohenberger W, Hess C, et al. Preoperative versus postoperative chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer: results of the German CAO/ARO/AIO-94 randomized phase III trial after a median follow-up of 11 years. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:1926–33. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.40.1836. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kuebler JP, Wieand HS, O’Connell MJ, Smith RE, Colangelo LH, Yothers G, et al. Oxaliplatin combined with weekly bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin as surgical adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II and III colon cancer: results from NSABP C-07. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2198–204. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.08.2974. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

