Involvement of ectonucleotidases and purinergic receptor expression during acute Chagas disease in the cortex of mice treated with resveratrol and benznidazole
- PMID: 34302569
- PMCID: PMC8410899
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-021-09803-9
Involvement of ectonucleotidases and purinergic receptor expression during acute Chagas disease in the cortex of mice treated with resveratrol and benznidazole
Abstract
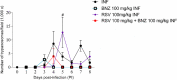
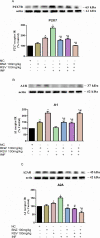
Chagas disease (CD) is caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. CD affects people worldwide, primarily in tropical areas. The central nervous system (CNS) is an essential site for T. cruzi persistence during infection. The protozoan may pass through the blood-brain barrier and may cause motor and cognitive neuronal damage. Once in the CNS, T. cruzi triggers immune responses that the purinergic system can regulate. Treatment for CD is based on benznidazole (BNZ); however, this agent has negative side-effects and is toxic to the host. For this reason, we investigated whether resveratrol (RSV), a potent antioxidant and neuroprotective molecule, would modulate purinergic signaling and RSV alone or in combination with BNZ would prevent changes in purinergic signaling and oxidative damage caused by T. cruzi. We infected mice with T. cruzi and treated them with RSV or BNZ for 8 days. Increases in ATP and ADP hydrolysis by NTPDase in the total cortex of infected animals were observed. The treatment with RSV in infected group diminished ATP, ADP, and AMP hydrolysis compared to infected group. The combination of RSV + BNZ decreased AMP hydrolysis in infected animals compared to the INF group, exerting an anti-inflammatory effect. RSV acted as a neuroprotector, decreasing adenosine levels. Infected animals presented an increase of P2X7 and A2A density of purine receptors. RSV reduced P2X7 and A2A and increased A1 density receptors in infected animals. In addition, infected animals showed higher TBARS and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels than control. RSV diminished ROS levels in infected mice, possibly due to antioxidant properties. In short, we conclude that resveratrol could act as a neuroprotective molecule, probably preventing inflammatory changes caused by infection by T. cruzi, even though the mice experienced high levels of parasitemia.
Keywords: A1R; ATP; Cellular stress; Resveratrol; T. cruzi.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective role of resveratrol mediated by purinergic signalling in cerebral cortex of mice infected by Toxoplasma gondii.Parasitol Res. 2020 Sep;119(9):2897-2905. doi: 10.1007/s00436-020-06795-0. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Parasitol Res. 2020. PMID: 32677001
-
Resveratrol impacts in oxidative stress in liver during Trypanosoma cruzi infection.Microb Pathog. 2021 Apr;153:104800. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104800. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Microb Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33609651 Review.
-
Effects of resveratrol on the differentiation fate of neural progenitor cells of mouse embryos infected with Trypanosoma cruzi.Microb Pathog. 2019 Jul;132:156-161. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.04.040. Epub 2019 Apr 25. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31029718
-
Elucidating the impact of low doses of nano-formulated benznidazole in acute experimental Chagas disease.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Dec 21;11(12):e0006119. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006119. eCollection 2017 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 29267280 Free PMC article.
-
Technological innovation strategies for the specific treatment of Chagas disease based on Benznidazole.Acta Trop. 2018 Sep;185:127-132. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.02.008. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Acta Trop. 2018. PMID: 29452113 Review.
Cited by
-
Resveratrol Alleviates Inflammatory Response Through P2X7/NLRP3 Signaling Pathway: In Silico and In Vitro Evidence from Activated Microglia.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 24;18(7):950. doi: 10.3390/ph18070950. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732240 Free PMC article.
-
E-NTPDases: Possible Roles on Host-Parasite Interactions and Therapeutic Opportunities.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Nov 9;11:769922. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.769922. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34858878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination Therapy and Phytochemical-Loaded Nanosytems for the Treatment of Neglected Tropical Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Sep 24;16(10):1239. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101239. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39458571 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Meyer H, Machado RD, Cintra WM. On the cultivation of Trypanosoma cruzi in tissue cultures of the spinal and sympathetic ganglion from the chick embryo. An Acad Bras Cienc. 1982;54:739–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

