Statins: a repurposed drug to fight cancer
- PMID: 34303383
- PMCID: PMC8306262
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-021-02041-2
Statins: a repurposed drug to fight cancer
Abstract
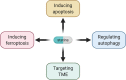
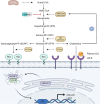
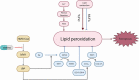
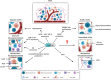
As competitive HMG-CoA reductase (HMGCR) inhibitors, statins not only reduce cholesterol and improve cardiovascular risk, but also exhibit pleiotropic effects that are independent of their lipid-lowering effects. Among them, the anti-cancer properties of statins have attracted much attention and indicated the potential of statins as repurposed drugs for the treatment of cancer. A large number of clinical and epidemiological studies have described the anticancer properties of statins, but the evidence for anticancer effectiveness of statins is inconsistent. It may be that certain molecular subtypes of cancer are more vulnerable to statin therapy than others. Whether statins have clinical anticancer effects is still an active area of research. Statins appear to enhance the efficacy and address the shortcomings associated with conventional cancer treatments, suggesting that statins should be considered in the context of combined therapies for cancer. Here, we present a comprehensive review of the potential of statins in anti-cancer treatments. We discuss the current understanding of the mechanisms underlying the anti-cancer properties of statins and their effects on different malignancies. We also provide recommendations for the design of future well-designed clinical trials of the anti-cancer efficacy of statins.
Keywords: Drug repurposing; Mevalonate pathway; Statins; Synergistic antitumor; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kodach LL, Jacobs RJ, Voorneveld PW, Wildenberg ME, Verspaget HW, van Wezel T, Morreau H, Hommes DW, Peppelenbosch MP, van den Brink GR, et al. Statins augment the chemosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells inducing epigenetic reprogramming and reducing colorectal cancer cell ‘stemness’ via the bone morphogenetic protein pathway. Gut. 2011;60(11):1544–1553. doi: 10.1136/gut.2011.237495. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

