Novel hydroxybenzylamine-deoxyvasicinone hybrids as anticholinesterase therapeutics for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 34304133
- PMCID: PMC8405574
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116311
Novel hydroxybenzylamine-deoxyvasicinone hybrids as anticholinesterase therapeutics for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
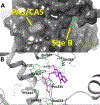
A series of novel 2-hydroxybenzylamine-deoxyvasicinone hybrid analogs (8a-8n) have been synthesized and evaluated as inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE), and as inhibitors of amyloid peptide (Aβ1-42) aggregation, for treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). These dual acting compounds exhibited good AChE inhibitory activities ranging from 0.34 to 6.35 µM. Analogs8g and 8n were found to be the most potent AChE inhibitors in the series with IC50values of 0.38 µM and 0.34 µM, respectively. All the analogs (8a-8n) exhibited weak BuChE inhibitory activities ranging from 14.60 to 21.65 µM. Analogs8g and 8n exhibited BuChE with IC50values of 15.38 µM and 14.60 µM, respectively, demonstrating that these analogs were greater than 40-fold more selective for inhibition of AChE over BuChE. Additionally, compounds8g and 8n were also found to be the best inhibitors of self-induced Aβ1-42 peptide aggregation with IC50values of 3.91 µM and 3.22 µM, respectively; 8g and 8n also inhibited AChE-induced Aβ1-42 peptide aggregation by 68.7% and 72.6%, respectively. Kinetic analysis and molecular docking studies indicate that analogs 8g and 8n bind to a new allosteric pocket (site B) on AChE. In addition, the observed inhibition of AChE-induced Aβ1-42 peptide aggregation by 8n is likely due to allosteric inhibition of the binding of this peptide at the CAS site on AChE. Overall, these results indicate that 8g and 8n are examples of dual-acting lead compounds for the development of highly effective anti-AD drugs.
Keywords: 2-Hydroxybenzylamine; Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors; Alzheimer’s disease; Aβ(1-42) peptide Aggregation; Deoxyvasicinone.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Camps P, El Achab R, Morral J, et al.New tacrine-huperzine A hybrids (huprines): highly potent tight-binding acetylcholinesterase inhibitors of interest for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J Med Chem. 2000;43(24): 4657–4666. - PubMed
-
- Simoni E, Bartolini M, Abu IF, et al.Multitarget drug design strategy in Alzheimer’s disease: focus on cholinergic transmission and amyloid-β aggregation. Future Med Chem. 2017;9(10): 953–963. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Ayllon MS, Silveyra MX, Andreasen N, Brimijoin S, Blennow K, Saez-Valero J. Cerebrospinal fluid acetylcholinesterase changes after treatment with donepezil in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 2007;101(6): 1701–1711. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Medical

