Dysregulation of host cell calcium signaling during viral infections: Emerging paradigm with high clinical relevance
- PMID: 34304899
- PMCID: PMC8299155
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2021.101004
Dysregulation of host cell calcium signaling during viral infections: Emerging paradigm with high clinical relevance
Abstract
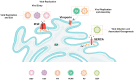
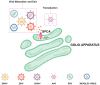
Viral infections are one of the leading causes of human illness. Viruses take over host cell signaling cascades for their replication and infection. Calcium (Ca2+) is a versatile and ubiquitous second messenger that modulates plethora of cellular functions. In last two decades, a critical role of host cell Ca2+ signaling in modulating viral infections has emerged. Furthermore, recent literature clearly implicates a vital role for the organellar Ca2+ dynamics (influx and efflux across organelles) in regulating virus entry, replication and severity of the infection. Therefore, it is not surprising that a number of viral infections including current SARS-CoV-2 driven COVID-19 pandemic are associated with dysregulated Ca2+ homeostasis. The focus of this review is to first discuss the role of host cell Ca2+ signaling in viral entry, replication and egress. We further deliberate on emerging literature demonstrating hijacking of the host cell Ca2+ dynamics by viruses. In particular, a variety of viruses including SARS-CoV-2 modulate lysosomal and cytosolic Ca2+ signaling for host cell entry and replication. Moreover, we delve into the recent studies, which have demonstrated the potential of several FDA-approved drugs targeting Ca2+ handling machinery in inhibiting viral infections. Importantly, we discuss the prospective of targeting intracellular Ca2+ signaling for better management and treatment of viral pathogenesis including COVID-19. Finally, we highlight the key outstanding questions in the field that demand critical and timely attention.
Keywords: COVID-19; Calcium; STIM1/Orai1; TPC2; VGCC; Virus.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Arduino D.M., Wettmarshausen J., Vais H., Navas-Navarro P., Cheng Y., Leimpek A., Ma Z., Delrio-Lorenzo A., Giordano A., Garcia-Perez C., Médard G., Kuster B., García-Sancho J., Mokranjac D., Foskett J.K., Alonso M.T., Perocchi F. Systematic identification of MCU modulators by orthogonal interspecies chemical screening. Mol. Cell. 2017;67:711–723. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.07.019. e7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnoult D., Bartle L.M., Skaletskaya A., Poncet D., Zamzami N., Park P.U., Sharpe J., Youle R.J., Goldmacher V.S. Cytomegalovirus cell death suppressor vMIA blocks Bax- but not Bak-mediated apoptosis by binding and sequestering Bax at mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2004;101:7988–7993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401897101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

