Promising Therapeutic Targets for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 34305919
- PMCID: PMC8299711
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.686155
Promising Therapeutic Targets for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
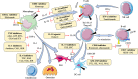
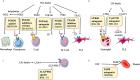
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic poly-articular chronic autoimmune joint disease that mainly damages the hands and feet, which affects 0.5% to 1.0% of the population worldwide. With the sustained development of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), significant success has been achieved for preventing and relieving disease activity in RA patients. Unfortunately, some patients still show limited response to DMARDs, which puts forward new requirements for special targets and novel therapies. Understanding the pathogenetic roles of the various molecules in RA could facilitate discovery of potential therapeutic targets and approaches. In this review, both existing and emerging targets, including the proteins, small molecular metabolites, and epigenetic regulators related to RA, are discussed, with a focus on the mechanisms that result in inflammation and the development of new drugs for blocking the various modulators in RA.
Keywords: epigenetic regulators; proteins; rheumatoid arthritis; small molecular metabolites; targets.
Copyright © 2021 Huang, Fu, Chen, Li, Huang and Liang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Szekanecz Z, Koch AE, Tak PP. Chemokine and Chemokine Receptor Blockade in Arthritis, a Prototype of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Netherlands J Med (2011) 69(9):356–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

