Whole-Genome Resequencing to Study Brucellosis Susceptibility in Sheep
- PMID: 34306007
- PMCID: PMC8297390
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.653927
Whole-Genome Resequencing to Study Brucellosis Susceptibility in Sheep
Abstract
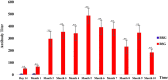
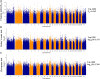
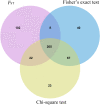
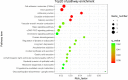
Brucellosis is a zoonotic disease and a major public health problem. However, the genetic mechanism of brucellosis in sheep remains unclear. In this study, serum samples were collected from 6,358 sheep from the F2 population (Dorper sheep ♂ × Hu sheep ♀), and antibody levels were continuously measured at 14 days and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10 months after administration of brucellosis vaccine. Finally, 19 brucellosis-resistant group (BRG) sheep and 22 brucellosis-susceptible group sheep (BSG) were screened for whole-genome sequencing. Using the fixation index, Fisher's exact test, and chi-square test, a total of 205 candidate SNP sites were identified. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis suggested that 138 candidate genes were significantly enriched in adherens junction (CTNNA3, PARD3, and PTPRM), cell adhesion molecules (NLGN1, CNTNAP2, NCAM1, and PTPRM), salivary secretion (LOC101102109, PRKG1, and ADCY2), and hippo signaling pathway (CTNNA3, YAP1, and PARD3). These findings provide valuable molecular markers for brucellosis resistance breeding in sheep and novel insights into the genetic mechanism of brucellosis resistance.
Keywords: FST; Fisher’s exact test; brucellosis; chi-square test; sheep; whole-genome resequencing.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Wu, Zhang, Li, Zhang, Li, Zhang, Zhao, Shi, Wang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

