Randomized Controlled Trial of Laparoscopic versus Open Radical Cystectomy in a Laparoscopic Naïve Center
- PMID: 34306069
- PMCID: PMC8279872
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/4731013
Randomized Controlled Trial of Laparoscopic versus Open Radical Cystectomy in a Laparoscopic Naïve Center
Abstract
Background: Laparoscopic radical cystectomy is a challenging surgical procedure; however, it has been largely abandoned in favor of the more intuitive robotic-assisted cystectomy. Due to the prohibitive cost of robotic surgery, the adoption of laparoscopic cystectomy is of relevance in low-resource institutes. Methodology. This is a randomized controlled trial comparing laparoscopic radical cystectomy (LRC) to open radical cystectomy (ORC) at a single institute. Each group included thirty patients. The trial was designed to compare both approaches regarding operative time, blood loss, transfusion requirements, length of hospital stay, time to oral intake, requirement of opioid analgesia, and complications.
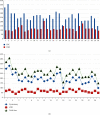
Results: LRC was associated with less hospital stay (9.8 vs. 13.8 days, P=0.001), less time to oral solid intake (6 vs. 8.6 days, P=0.031), and lower opioid requirements (23.3% vs. 53.3%, P=0.033). There was a trend towards lower blood loss and transfusion requirements, but this did not reach statistical significance. Overall complication rates were comparable.
Conclusion: Laparoscopic radical cystectomy was associated with comparable postoperative outcomes when compared to ORC in the first laparoscopic cystectomy experience in our center. Benefitting from the assistance of an experienced laparoscopic surgeon is recommended to shorten the learning curve.
Copyright © 2021 Waleed Mohamed Fadlalla et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of laparoscopic approach in radical cystectomy from implementation to consolidation: Internal validation.Actas Urol Esp (Engl Ed). 2020 Mar;44(2):62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.acuro.2019.07.002. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Actas Urol Esp (Engl Ed). 2020. PMID: 31759755 English, Spanish.
-
A prospective randomised controlled trial of laparoscopic vs open radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: perioperative and oncologic outcomes with 5-year follow-upT Lin et al.Br J Cancer. 2014 Feb 18;110(4):842-9. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.777. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24407192 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Does previous abdominal surgery adversely affect perioperative and oncologic outcomes of laparoscopic radical cystectomy?World J Surg Oncol. 2018 Jan 17;16(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12957-018-1317-6. World J Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29343302 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effectiveness of open, laparoscopic and robot-assisted radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2020 Jun;72(3):251-264. doi: 10.23736/S0393-2249.20.03680-2. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2020. PMID: 32083418
-
Robot-assisted vs open radical cystectomy for bladder cancer in adults.BJU Int. 2020 Jun;125(6):765-779. doi: 10.1111/bju.14870. BJU Int. 2020. PMID: 31309688
Cited by
-
Incisional hernia incidence following laparoscopic versus open abdominal surgery: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Hernia. 2025 Apr 30;29(1):152. doi: 10.1007/s10029-025-03347-2. Hernia. 2025. PMID: 40304805
-
Global cancer surgery in low-resource settings: A strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats analysis.Cancer. 2023 Mar 1;129(5):671-684. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34630. Epub 2023 Jan 3. Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36597652 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Matsumoto K., Tabata K.-i., Hirayama T., et al. Robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy is a safe and effective procedure for patients with bladder cancer compared to laparoscopic and open surgery: perioperative outcomes of a single-center experience. Asian Journal of Surgery. 2019;42(1):189–196. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2017.11.002. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

