Association between Lipid Profiles and Serum Urate: A Cross-Sectional Study in Southwestern China
- PMID: 34306070
- PMCID: PMC8285201
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/2741131
Association between Lipid Profiles and Serum Urate: A Cross-Sectional Study in Southwestern China
Abstract
Objective: The relationship between lipid profiles and serum urate has not been fully investigated. This study aims to investigate the sex- and age-specific association between lipid profiles and serum urate.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study involving 122,351 participants aged 18-99 years from a check-up centre in Southwestern China. Generalized additive models and smooth curve fitting were conducted to explore the association between components of lipid profiles and serum urate. Furthermore, multivariate linear and logistic regression models were also performed.
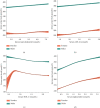
Results: In generalized additive models, the fitted smoothing curves showed that serum urate fluctuated in a small range with total cholesterol, LDL-C, or HDL-C raising. After adjusting for confounders, the differences in serum urate progressively increased with raising serum triglycerides quartiles. The likelihood (odds ratio, OR) for developing serum urate > 420 μmol/L significantly increased in the highest quartile of triglycerides than in the lowest quartile, in hypertriglyceridemia than in normal triglycerides, and with 1 mmol/L increment in triglycerides in all sex- and age-specific groups. Furthermore, the increased OR (95% confidence interval) was higher in females than in males compared with their respective controls.
Conclusions: Serum urate and the likelihood for developing serum urate >420 μmol/L increased with triglycerides raising. Females were in a higher likelihood for developing serum urate >420 μmol/L than males with raising triglycerides. With changes in total cholesterol, LDL-C, or HDL-C, serum urate fluctuated in a small range.
Copyright © 2021 Jiying Qi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is superior to triglycerides and other lipid ratios as an indicator of increased urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio in the general population of China: a cross-sectional study.Lipids Health Dis. 2021 Feb 15;20(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12944-021-01442-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2021. PMID: 33588849 Free PMC article.
-
[The gender features of disorders of composition of lipids of blood serum in patients with chronic pathology of kidneys.].Klin Lab Diagn. 2018;63(3):152-158. doi: 10.18821/0869-2084-2018-63-3-152-158. Klin Lab Diagn. 2018. PMID: 30673194 Russian.
-
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN SERUM URIC ACID LEVEL AND BODY MASS INDEX IN SEX- AND AGE-SPECIFIC GROUPS IN SOUTHWESTERN CHINA.Endocr Pract. 2019 May;25(5):438-445. doi: 10.4158/EP-2018-0426. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Endocr Pract. 2019. PMID: 30657365
-
Effects of α-linolenic acid intake on blood lipid profiles:a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021;61(17):2894-2910. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1790496. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32643951
-
Almonds have a neutral effect on serum lipid profiles: a meta-analysis of randomized trials.J Am Diet Assoc. 2009 May;109(5):865-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2009.02.014. J Am Diet Assoc. 2009. PMID: 19394473 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin use and gout risk among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a real-world cohort study in Shanghai, China.Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Nov;42(11):3067-3073. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06684-8. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37400692
-
Fatty acid oxidation-induced HIF-1α activation facilitates hepatic urate synthesis through upregulating NT5C2 and XDH.Life Metab. 2024 May 17;3(5):loae018. doi: 10.1093/lifemeta/loae018. eCollection 2024 Oct. Life Metab. 2024. PMID: 39872146 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-ancestry genome-wide association study and evaluation of polygenic scores of LDL-C levels.J Lipid Res. 2025 Mar;66(3):100752. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2025.100752. Epub 2025 Feb 3. J Lipid Res. 2025. PMID: 39909172 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between lipid-lowering drugs and urate and gout outcomes: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 24;15:1398023. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1398023. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39926389 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-related differences in the hypertriglyceridemic-waist phenotype in association with hyperuricemia: a longitudinal cohort study.Lipids Health Dis. 2023 Mar 11;22(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01795-2. Lipids Health Dis. 2023. PMID: 36906544 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

